Sudo and su are commonly used commands in Linux terminals. They both allow users to execute tasks with root privileges, but they are approached differently. In this article, we will explore the key differences between sudo and su and how they function.
What is Sudo?
Sudo is a setuid binary located in the root directory. It enables users to execute root commands on behalf of authorized users. To use sudo, users need to input their own passwords to execute system commands as a root user.
You are viewing: Understanding the Differences Between Sudo and Su
Who Can Execute Sudo?
Read more : What Disease Does David Gilmour Have
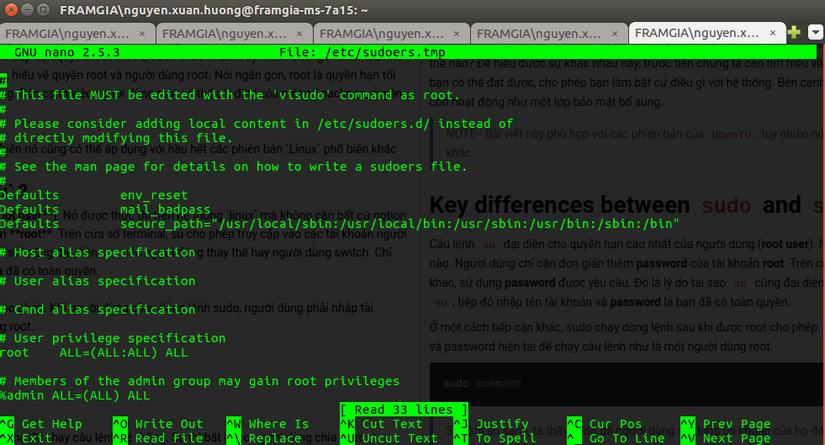
To determine which users can use sudo, you can run the following command: $ sudo /usr/sbin/visudo. This command will open the visudo file, where you can add or remove users from the sudo access list. By default, the list includes the root user with full access.
Granting sudo access requires caution, as giving unrestricted access to inexperienced users can cause significant harm. For example, modifying the visudo file to include adam ALL=(ALL) ALL, tom ALL=(ALL) ALL, or mark ALL=(ALL) ALL allows those users to have unrestricted sudo access.
Parameters of Sudo
Sudo allows for flexible configuration, where the number of commands that can be run can be specified precisely. The syntax for configuring sudo is as follows:
User_name Machine_name=(Effective_user) commandRead more : What Font Does Notion Use
The syntax includes:
- User_name: The name of the user
- Machine_name: The name of the server where the sudo command is valid. This is especially useful when managing multiple servers.
- (Effective_user): The user who is allowed to execute the system commands. This column allows you to grant users the ability to run system commands.
- Command: The command or set of commands that the user can execute.
Conclusion
In summary, sudo and su provide different ways to access root privileges in Linux. While su allows users to switch to the root user by entering the root password, sudo allows users to run commands with their own account credentials. It is crucial to configure sudo access carefully to maintain security and prevent unauthorized access.
To learn more about the differences between sudo and su and how to configure sudo in Linux, check out the following references:
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHAT