DC Machine:
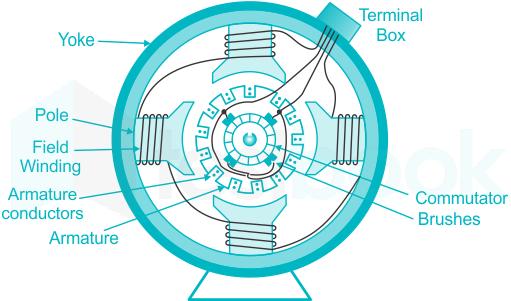
The above figure shows constructional details of a simple 4-pole DC machine.
A DC machine consists of two basic parts; stator and rotor. Basic constructional parts of a DC machine are described below.
Brushes:
-
The brush in a DC machine is a component that collects the current from the moving parts and feeds it to the stationary circuit
- Brushes are usually made from carbon or graphite, but copper brushes are preferred in low voltage high current requirements.
-
Brush contact loss attributes to the resistance between the surface of the brush and the commutator
-
This loss is mostly enclosed in armature copper loss
- As copper losses depend on load current, brush contact losses also depend on load current; These are directly proportional to the current
Yoke:
- The outer frame of a dc machine is called a yoke.
- It is made up of cast iron or steel.
- It not only provides mechanical strength to the whole assembly but also carries the magnetic flux produced by the field winding.
Read more : Which Art Group Is The National Treasure Of Canada
Poles and pole shoes:
- Poles are joined to the yoke with the help of bolts or welding.
- They carry field winding and pole shoes are fastened to them.
- Pole shoes serve two purposes; (i) they support field coils and (ii) spread out the flux in the air gap uniformly.
Field winding:
- They are usually made of copper.
- Field coils are former wounds and placed on each pole and are connected in series.
- They are wound in such a way that, when energized, they form alternate North and South poles.
Armature core:
- Armature core is the rotor of a dc machine. It is cylindrical in shape with slots to carry armature winding.
- The armature is built up of thin laminated circular steel disks for reducing eddy current losses.
- Armature core is made of silicon steel laminations which are insulated from each other by insulating varnish coating. These laminations are used to reduce eddy current losses.
- It may be provided with air ducts for the axial air flow for cooling purposes.
- Armature is keyed to the shaft.
Armature winding:
- It is usually a former wound copper coil which rests in armature slots.
- The armature conductors are insulated from each other and also from the armature core.
- Armature winding can be wound by one of the two methods; lap winding or wave winding.
- Double layer lap or wave windings are generally used. A double layer winding means that each armature slot will carry two different coils.
Commutator and brushes:
- In the case of the DC generator, the commutator is used to convert generated AC in armature into DC.
- In the case of DC motor, the commutator is used to convert DC to A.C
- Due to the limitation of the commutator dc generators are not usually designed beyond 650 V
- The physical connection to the armature winding is made through a commutator-brush arrangement.
- The function of a commutator in a dc generator is to collect the current generated in armature conductors.
- While in the case of a dc motor, the commutator helps in providing current to the armature conductors.
- A commutator consists of a set of copper segments which are insulated from each other.
- The number of segments is equal to the number of armature coils. Each segment is connected to an armature coil and the commutator is keyed to the shaft.
- Brushes are usually made from carbon or graphite, but copper brushes are preferred in low voltage high current requirements.
- They rest on commutator segments and slide on the segments when the commutator rotates keeping the physical contact to collect or supply the current.
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH
