If you’re in the market for a new telescope, you’re sure to run into the question of refractor vs. reflector telescopes. How do they work? Which one is better? In this article, we’ll make sense of these questions to help make your decision process easier.
The first step in deciding on a refractor vs. reflector telescope is determining what you want to see. Refractor telescopes utilize specialized lenses that make them a favorite for deep space objects like galaxies and nebulae. In contrast, reflector telescopes are more popular with larger and brighter objects like the Moon and planets because they use mirrors that provide more sensitivity to all wavelengths.
You are viewing: Which Telescope Is Better Reflector Or Refractor
Let’s get to know them more below!
REFRACTOR TELESCOPES
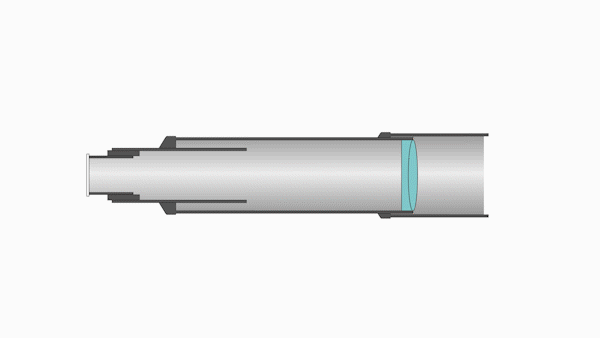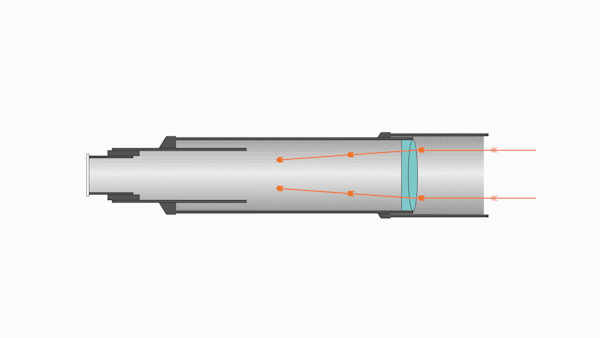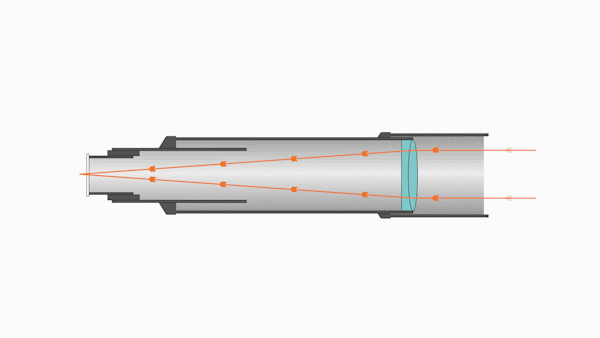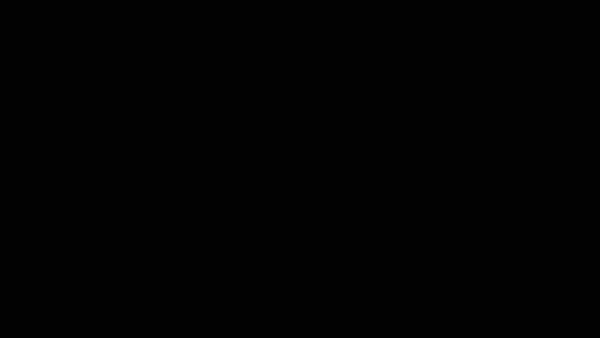
Refractors utilize specially designed lenses to focus the light into an image. Most refractors contain two lenses:
- The larger is called the objective lens, which focuses incoming light inside the tube
- The smaller is called the eyepiece lens, which focuses the light for viewing
The objective lens is located near the far end of the telescope tube, and the larger the lens, the longer the optical tube must be to bring the image into focus.
The length and size of the lens of a refractor, combined with the fact that large lenses can be difficult and expensive for glassmakers to manufacture at high quality, means that larger refractors can get rather expensive. For this reason, most refractors tend to be smaller-aperture models, making refracting telescopes one of the most portable telescopes on the market.
A good beginner refractor is the Celestron PowerSeeker 80EQ telescope, which is great for both celestial and terrestrial viewing.
REFRACTOR TELESCOPES AND CHROMATIC ABERRATION

One drawback of refractors is chromatic aberration, which is color fringing caused by the fact that different wavelengths of light are refracted at different angles by the same lens. Specifically, a wave of light contains many different wavelengths. When these enter the lens, they split from each other and arrive at slightly different angles. To the observer, the image will contain distinct coloration at the edges.
Most low-cost refractors are “doublets,” which may have color fringing, whereas “triplet” refractors are designed to eliminate this issue; this three-lens system is referred to as an apochromatic refractor telescope.
Still, whether a doublet or triplet, refractors are solidly built scopes. Their non-movable lenses make for a sturdy design that doesn’t need much maintenance beyond the occasional cleaning.
Pros of Refactor Telescopes
- Low image distortion
- Images are right-side-up
- Lenses don’t require collimation
- A closed system means low maintenance and very little cleaning
- Beginner friendly.
Cons of Refractor Telescopes
- Chromatic aberration (can be corrected with apochromatic telescopes)
- Smaller apertures due to high cost
- Less light collected
- Wider apertures are very expensive
REFLECTOR TELESCOPES
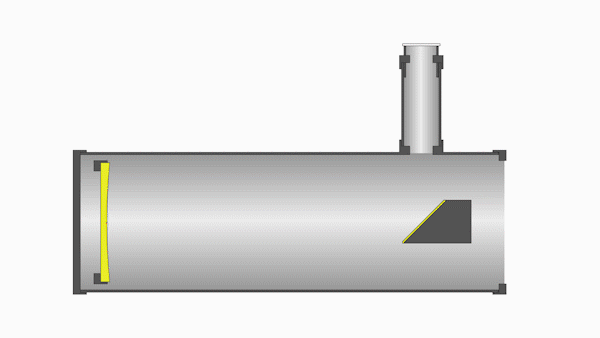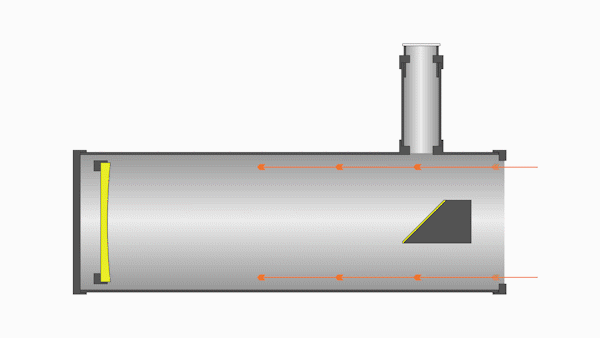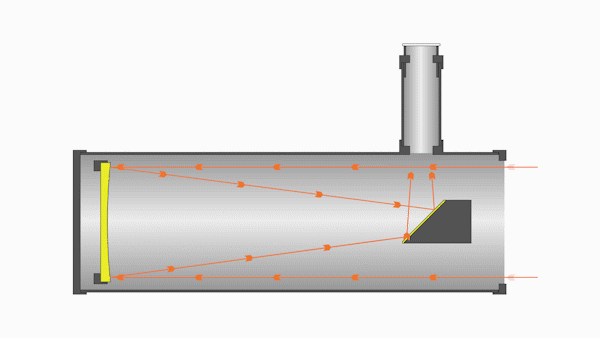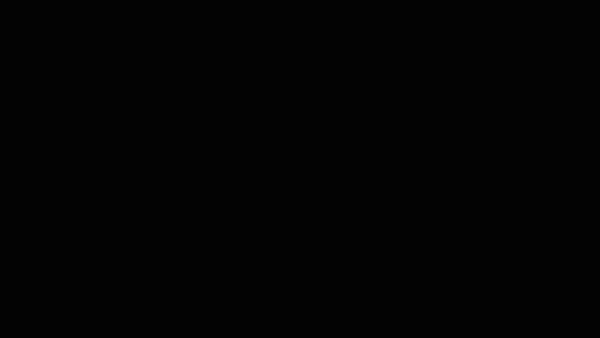
Whereas refractors use lenses, reflectors use mirrors. These mirrors reflect light at various angles within the optical tube, extending the overall light path.
A reflector consists of a primary mirror located at the opposite end of the telescope from the aperture and a smaller secondary mirror near where the reflected light converges. This secondary mirror reflects the light toward the eyepiece or CCD.
It’s relatively common for reflectors to be less expensive than refractors since manufacturing large mirrors is usually more affordable than manufacturing large lenses.
Additionally, reflector telescopes are not susceptible to color fringing in the same way that doublet refractors are. If you’re looking for more bang for your buck in terms of aperture, reflectors are a great way to go. This is especially true for Dobsonians, which come with their own easy-to-use rocker-box mount.
Reflector telescopes can provide great value and offer many conveniences. They can also come in a variety of sizes, some of which can get quite large. With this in mind, purchasing the largest reflector you can afford is a great, low-cost way to get a high-aperture scope. Just make sure you can store and transport it safely.
Considerations About Reflector Telescopes
There are some things to consider about the reflector design. By default, the image you see through a reflector’s eyepiece will be upside down. For this reason, you’ll want to use your scope’s finder to line it up with the objects you want to see before looking through the eyepiece. Most modern reflecting telescopes come with a finderscope or a red dot finder, so you most likely won’t have to make an additional purchase to acquire this.

Additionally, reflector telescopes will sometimes require a process called collimation, which consists of adjusting the reflector’s mirrors to ensure they stay in proper alignment with each other.
When properly maintained, a large reflector is a great way to view smaller or faraway objects with great clarity. It provides excellent value for achieving high-aperture viewing.
Different Reflector Designs
There are several popular reflecting telescope designs:
1. Newtonian
Read more : Which Is More Reliable Kia Or Hyundai
Lovingly referred to as a “Newt,” this is the simplest type of reflector: a parabolic mirror that reflects the light back to a secondary mirror at a 45º angle, which directs it to an eyepiece or camera. These are excellent for beginners, have short focal ratios, and can have large apertures. However, they require regular collimation and are quite heavy.
2. Dobsonian
The Dobsonian (or “Dob”) is simply a Newtonian telescope mounted on a modified alt-azimuth mouth, making it relatively easy to use. This mount lets it rotate freely and removes the need for a tripod. Dobs are great for visual astronomy and can have large apertures, though they are not well-suited to deep-sky astrophotography and are large and heavy.
3. Richey-Chretién (RC)
A variation of the Cassegrain design, the RC telescope uses hyperbolic instead of parabolic mirrors. This eliminates coma almost entirely, though they suffer from astigmatism (or “wings” on either side of bright stars). They are great for deep-sky astrophotography but are more expensive and not well-suited to planetary work due to how the large central obstruction decreases contrast.
4. Dall-Kirkham and other Cassegrains
These designs are less common but are excellent for planetary astronomy. They use all-mirror designs instead of the lenses introduced by Schmidt-Cassegrains and refractors. They suffer from no chromatic aberration and have long focal ratios, though they are expensive and have a narrow range of uses.
Pros of Reflector Telescopes
- Great for beginners
- Big aperture for observing deep-sky objects
- No chromatic aberration due to the use of mirrors
- Capture significant amounts of light
Cons of Reflector Telescopes
- Optical quality can disappoint
- Mirrors require collimations and cleaning
- Open tube design leaves equipment vulnerable to humidity, dust, etc.
- Heavy, large design
Reflector vs. Refractor: Which is Better?
If you are interested in astrophotography, purchasing a refractor is probably a better option. This is because of its specialized optic design, which captures deep space objects like galaxies and nebulae. Choose an apochromatic model if you want to avoid chromatic aberrations.
A reflector telescope is the better choice if you are interested in brighter celestial objects like the Moon or planets. Due to reflectors’ larger apertures at similar prices, they’ll usually be the best choice for almost all things visual. They can also be great for deep sky astrophotography, but we don’t recommend them for beginners because they require a lot of maintenance and precise setting up.
Refractors, on the other hand, can also be great for visual, but they get very expensive for similar-size apertures as reflectors. But they are excellent for deep sky astrophotography and are what we recommend for all beginners getting started in deep sky imaging.
Contact us if you have any questions — our sales team is knowledgeable, friendly, and ready to help.
Check out our telescope buying guide for some step-by-step help. For beginners in astrophotography, check out our video on how to build an astrophotography setup to get started!
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH