Geometry defines a dimension as the number of coordinates needed to specify a point on the object. (“The Differences Between 1D, 2D & 3D Pictures”, 2018)
Dimensions (in geometry) is the number of values required to locate points in a shape.
You are viewing: Which Of The Following Are Zero-dimensional Or One-dimensional Figures
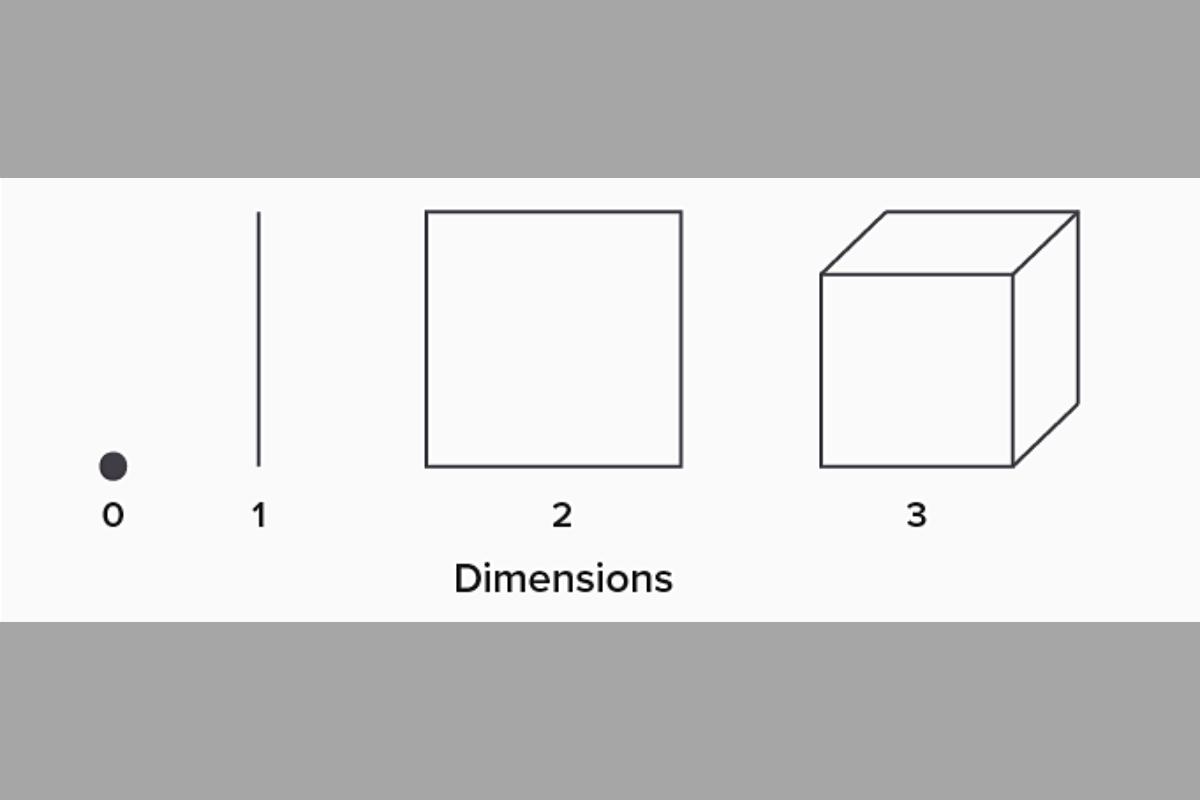
Zero Dimension (0D): A point has no dimensions. It has no length, width, or height. It has no size and tells about the location only. We usually represent it by a dot.
One Dimension (1D): A line segment drawn on a surface is an example of a one-dimensional object. It has only length and no width. To specify a point on the line, you only need to one value, the length.
Two Dimension (2D): This applies to flat plane shapes or objects with two dimensions, length and width, but no depth or thickness. We need two values to find a point in such a plane. Examples include; circle, triangle, square, rectangle, polygon, etc.
Read more : Navigating Kansas City International Airport (MCI) with Ease
Three Dimension (3D): This applies to solid figures or objects or shapes that have three dimensions-length, width and height. Three-dimensional shapes have thickness or depth. 3D, therefore, applies to objects with volume. An example is a cube which has length, width and height.
In surveying, we use 3D where the x, y location of a point in space can have several z (elevation values). E.g. consider a point in a tall building. At the same x, y location, it can have several elevations (z) values on different floors.
Two and a half Dimension (2.5D): (In the surveying profession). We reference the location of a point in space using x, y, z values where z denotes the elevation. In 2.5D, each x, y location can only have one z value. We apply 2.5D when generating DEMs and TINs to display the topography.
Four Dimension (4D): We refer to Time to as the fourth dimension. Geographical phenomena can change with time. Defining the time when we collect data is therefore important in surveying.
Note that in other fields, they define the fourth dimension differently. Artists and writers often think of the fourth dimension as the life of the mind. For others, the fourth dimension is metaphysical.
References
Read more : Which Of These Works Exemplifies The Neo-expressionist Style
· The Differences Between 1D, 2D & 3D Pictures. Sciencing. (2018). Retrieved 25 November 2020, from https://sciencing.com/differences-between-1d-2d-3d-pictures-10027643.html.
· What is 1D, 2D, 3D, and 4D? How is it easily understood by a beginner?. Quora.com. (2018). Retrieved 25 November 2020, from https://www.quora.com/What-is-1D-2D-3D-and-4D-How-is-it-easily-understood-by-a-beginner.
· What is Dimensions? – Definition, Facts and Examples. Splashlearn.com. Retrieved 25 November 2020, from https://www.splashlearn.com/math-vocabulary/geometry/dimensions.
· GEO 465/565 Lecture 14. Dusk.geo.orst.edu. Retrieved 25 November 2020, from http://dusk.geo.orst.edu/gis/lec14_3d.html.
· Dimensions. Mathsisfun.com. Retrieved 25 November 2020, from https://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/dimensions.html.
#staysafe
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH