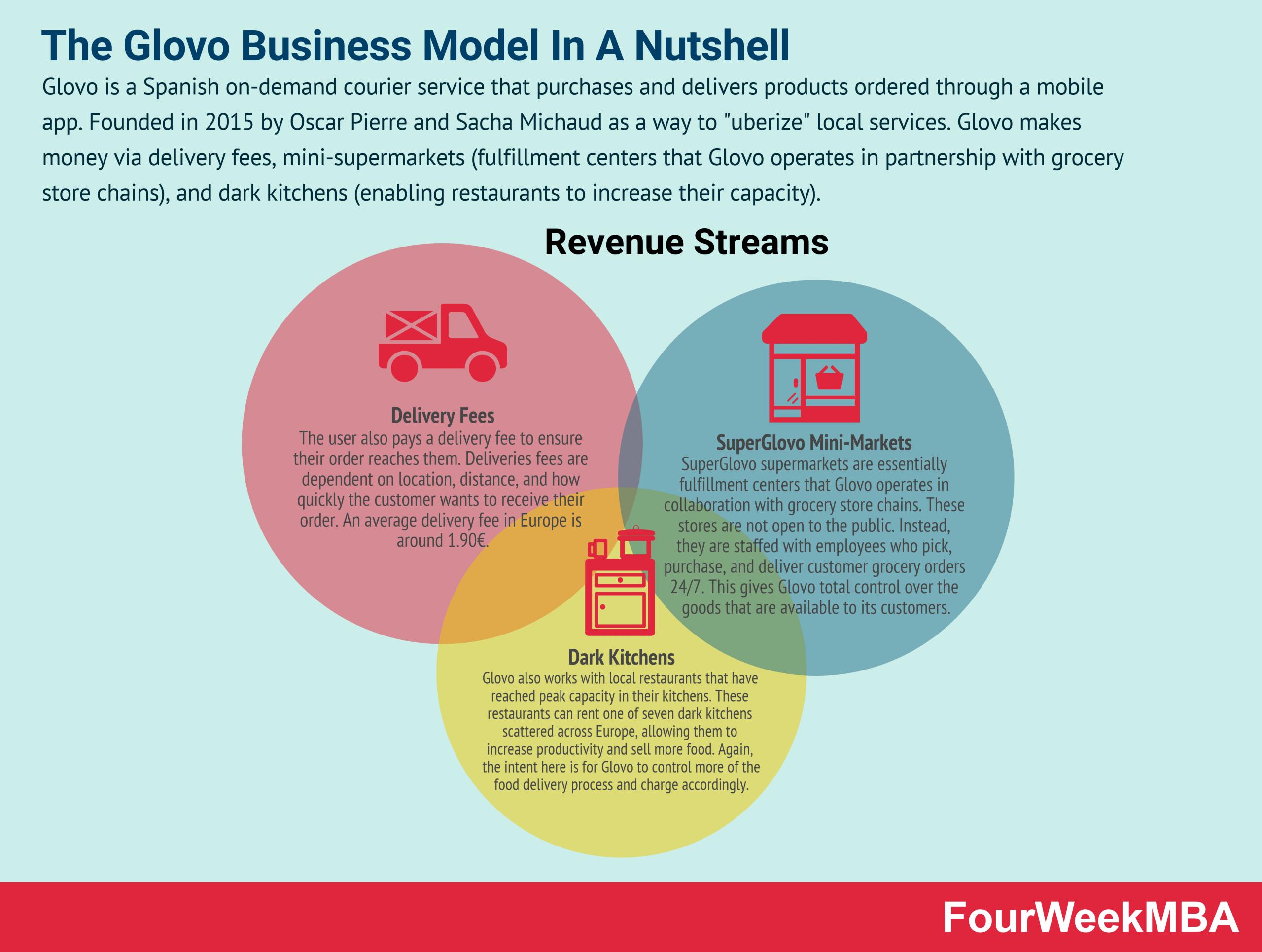
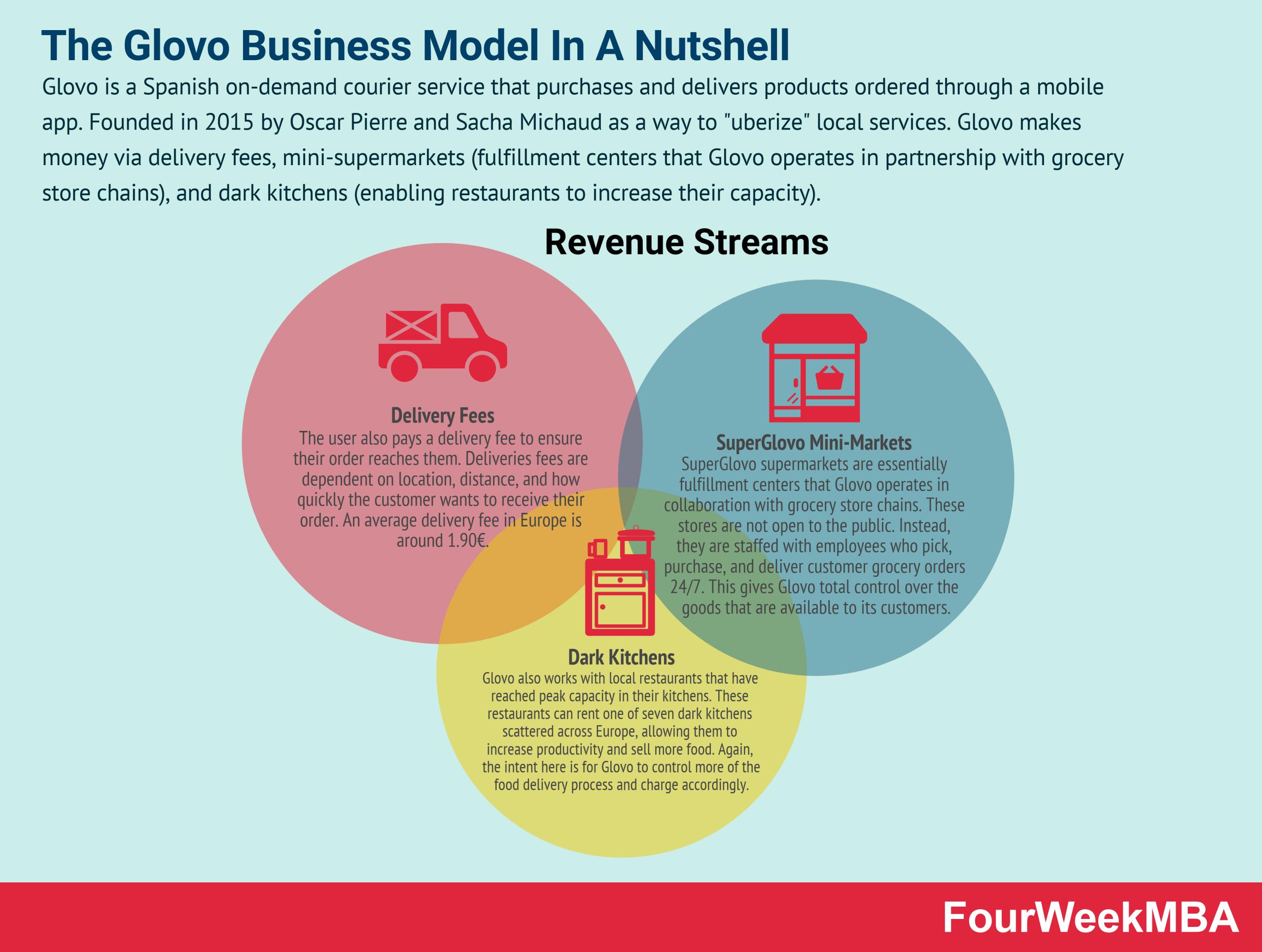
Glovo is a Spanish on-demand courier service that purchases and delivers products ordered through a mobile app. Founded in 2015 by Oscar Pierre and Sacha Michaud as a way to “uberize” local services. Glovo makes money via delivery fees, mini-supermarkets (fulfillment centers that Glovo operates in partnership with grocery store chains), and dark kitchens (enabling restaurants to increase their capacity).
Origin Story
Glovo is a Spanish on-demand courier service that purchases and delivers products ordered through a mobile app.
You are viewing: How Does Glovo Make Money
The company was founded in 2015 by Oscar Pierre and Sacha Michaud, primary in response to the uberization of local services.
It is perhaps most well-known for its food delivery service, but the company has a mission to develop an urban lifestyle product.
This encompasses the delivery of pharmacy goods, groceries, jewelry, flowers, courier parcels, and desserts among other options.
Indeed, Glovo markets itself as able to deliver anything. It will for example buy a customer a size 10 dress from Zara and deliver it to their doorstep.
Such is Glovo’s success that it has expanded globally with operations focused on Europe, Africa, and South America.
Securing the funding that enabled the company to attain a significant market share in the very competitive delivery industry.
Glovo’s Value Proposition:
- Convenience: Glovo provides a convenient and efficient way for customers to order and receive a wide range of products, from food to groceries, pharmacy items, and more, all through a single mobile app.
- Versatility: The platform offers versatility in delivery options, allowing users to order from restaurants, local stores, supermarkets, and even dark kitchens. This versatility caters to a broad spectrum of customer needs.
- Urban Lifestyle Enhancement: Glovo aims to enhance the urban lifestyle by offering a diverse selection of goods and services that can be delivered directly to customers’ doorsteps, simplifying daily tasks and saving time.
- Global Reach: Glovo’s global presence across Europe, Africa, and South America makes it accessible to customers in multiple regions, providing an international solution for on-demand deliveries.
Customer Segments:
- Consumers: Individuals and households seeking convenient and quick delivery of various products, including meals, groceries, pharmacy items, electronics, and more.
- Restaurants: Restaurants looking to expand their delivery services and reach a broader customer base through Glovo’s platform.
- Local Stores: Retail businesses, including grocery stores, electronics shops, and pharmacies, partnering with Glovo to offer delivery services to their customers.
- Couriers: Independent couriers or delivery drivers who collaborate with Glovo to earn income by fulfilling delivery orders.
Distribution Strategy:
- Mobile App: Glovo’s mobile application serves as the primary distribution channel, allowing users to browse products, place orders, and track deliveries. It also provides a platform for partner businesses to manage orders and for couriers to accept and complete delivery assignments.
- Website: Glovo’s website complements its mobile app by offering users an alternative platform for accessing the service and placing orders.
Marketing Strategy:
- User Acquisition: Glovo invests in user acquisition strategies, including digital advertising, social media marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO), to attract new customers to its platform.
- Partnership Marketing: The company collaborates with restaurants, local stores, and supermarket chains to encourage them to join its platform, expanding the range of products available for delivery.
- Promotions and Discounts: Glovo runs promotional campaigns and offers discounts to incentivize users to place orders and engage with the platform regularly.
- Geographic Expansion: To grow its market reach, Glovo strategically enters new cities and regions, expanding its presence and user base.
- User Engagement: Glovo engages with its users through email marketing, personalized recommendations, and push notifications to keep them informed about promotions, new features, and order updates.
Glovo revenue generation
Glovo drives revenue by charging its partners a fee. This fee is typically 22-30% of the total value of the food or product being delivered. The exact fee is agreed upon between Glovo and each business.
Read more : How Much To Rent A Mizuno Glove
A portion of this fee is given to Glovo couriers based on the distance they cover while delivering.
Delivery fee
The user also pays a delivery fee to ensure their order reaches them. Deliveries fees are dependent on location, distance, and how quickly the customer wants to receive their order.
An average delivery fee in Europe is around 1.90€.
SuperGlovo mini-supermarkets
SuperGlovo supermarkets are essentially fulfillment centers that Glovo operates in collaboration with grocery store chains.
These stores are not open to the public. Instead, they are staffed with employees who pick, purchase, and deliver customer grocery orders 24/7. This gives Glovo total control over the goods that are available to its customers.
These stores are still a relatively new concept and as such, are only offered in Madrid and Barcelona. However, the company hopes to expand its rapid delivery service by using the efficiency of a McDonald’s drive-through as inspiration. Pickers are being trained to select an entire customer order before the courier arrives to collect it.
Glovo is also targeting every day, household items to drive revenue in a relatively underserved segment. This includes items such as bread, milk, cereal, and water.
Dark kitchens
Glovo also works with local restaurants that have reached peak capacity in their kitchens. These restaurants can rent one of seven dark kitchens scattered across Europe, allowing them to increase productivity and sell more food.
Again, the intent here is for Glovo to control more of the food delivery process and charge accordingly.
Key takeaways
- Glovo is a Spanish on-demand courier service. Although most well-known for delivering restaurant food, the company will deliver almost anything including clothes, pharmacy goods, and jewelry.
- Glovo charges its customers a delivery fee and also takes a 22-30% commission from each participating business. The company gives a portion of this commission to the courier, depending on the distance covered.
- Glovo is also in the process of creating supermarket fulfillment stores. These stores are attended by pickers who collect orders for common household purchases and deliver them 24/7. The company also makes money by offering kitchen space to restaurants that require extra space.
Read more : How To Break In A Third Baseman Glove
Read Next: Last-Mile Problem, Amazon Business Model, Grubhub Business Model, Uber Business Model, Uber Eats Business Model, How Does Postmates Make Money, How Does OpenTable Make Money.
Connected Last-Mile Delivery Business Models
Deliveroo Business Model
DoorDash Business Model
Glovo Business Model
GrubHub Business Model
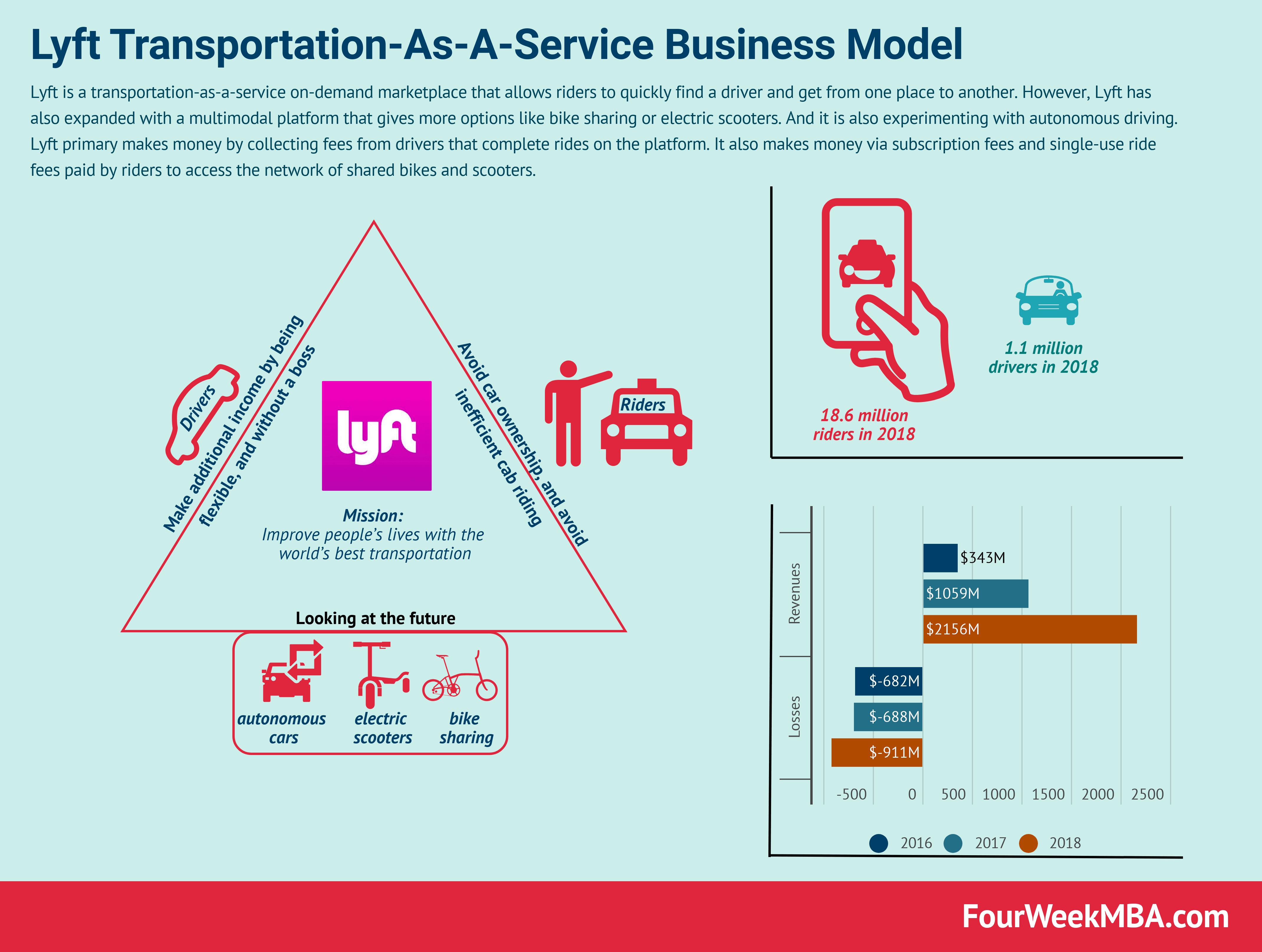
Lyft Business Model
OpenTable Business Model
Postmates Business Model
Uber Eats Business Model
Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: HOW
