What Is ‘EDI Capable’?
EDI capability is the smooth exchange of electronic business documents that meet the EDI compliance standards of your trading partners. Two ways to become EDI capable are to implement an on-premise EDI solution on your own (or third-party data center) or purchase the necessary EDI tools from an EDI cloud service.
In the simplest terms, being EDI capable is the ability to run an EDI software for streamlined business communication with your partners, vendors, suppliers, customers, etc. While the term “EDI capable” might be straightforward, there are many business influencers who don’t know what it takes to accommodate and leverage this vital logistics communication technology.
You are viewing: What Is Edi Capable
By the end of implementation, an enterprise must be ready to send and receive electronic documents such as X12, EDIFACT, Tradacoms, ODETTE, EANCOM, HIPAA, VDA, and others. And while these document standards are fundamental, there’s much more to EDI. The electronic data interchange implementation process is a broad B2B integration strategy that ultimately boosts high-value business results. True EDI systems include a set of governance, management, visibility, and onboarding processes.
What it Means to be EDI Capable
The supply chain and EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) have both been described as the lifeblood of logistics.
And it’s a very fitting description. Think of the supply chain as the body’s circulatory system. EDI communication standards is the blood coursing through, making it go. All the various EDI messages are the red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, and platelets.
For any organization to fully grasp the chaotic yet essential supply chain, it needs EDI to make sense of it all. Take it from an EDI company that optimizes countless supply chains, you really can’t have one without the other.
But most organizations that need to utilize EDI, already do in some, way, shape, or form. It’s not like EDI is some hidden secret just waiting to be unearthed. After all, the critical data communications standard has been an essential logistics tool for many, many decades now.
So, in 2024, the question isn’t really “Is your company using EDI?” Here’s the real question: Is your company EDI capable of modern business demands?
True, there may be a handful of companies not taking advantage of EDI solutions or that have regrettably jumped ship for the somewhat exaggerated, un-contextualized API potential, but unless you’re a fledgling organization, the issue mostly lies with modernization or an upgrade of some sort in EDI format capabilities. With so many technical innovations across the increasingly digital landscape, many businesses are discovering their current EDI solutions just aren’t keeping up.
And for any company that has just started doing EDI or is considering it to meet a trading partner requirement/industry regulation, EDI can seem like an uphill battle to meet the required B2B transaction protocols, document types, communication methods, security mandates, and other aspects.
EDI capability is no doubt complex. But below is everything a company needs to know to make sense of it all.
How to Become EDI Capable
EDI’s main goal in life is to make everything about business and logistics workflows easier through standardization, automation, integration, and simplification of critical data exchanges. But any EDI connoisseur knows getting there takes specialized expertise and integration with other business processes.
And there are several ways to approach EDI capabilities that meet modern business demands. Here is a 4-step process to becoming EDI capable starting with the understanding of your trading partners’ requirements.
4-Steps to Become EDI Capable
1. Become Familiar with Your Trading Partners’ Compliance RequirementsTo achieve EDI compliance, the first step is to clearly understand the compliance requirements imposed by your trading partners. Familiarize yourself with the specific EDI formats expected for each document exchange. This establishes a foundation for seamless and effective communication.
2. Determine a Flexible EDI Approach (In-House, Outsourced, Both)After gaining insight into the expectations of your trading partners, make a decision regarding the management of EDI operations. Consider whether to handle EDI tasks internally or delegate them to an external service provider.Evaluate factors such as available resources, expertise, and associated costs. If you possess the necessary skills and infrastructure, you may choose to maintain EDI processes in-house. On the other hand, you can collaborate with a proficient EDI service provider for guidance and support.
3. Explore EDI Solutions Suitable to Your ApproachAfter determining your EDI approach, proceed to investigate the necessary tools of an EDI solution. This process involves research, Q&A discussion, and demonstration of the solution capabilities. All of these should align with your organizational expertise and resources while satisfying the expectations of your partners.
4. Thoroughly Test Your EDI SolutionBefore embarking on the EDI journey, it is imperative to thoroughly test your solution. Comprehensive testing verifies the effectiveness of your chosen EDI solution and configurations to facilitate document exchange with your trading partners. Collaborate with technical support to rigorously test, identify, and resolve any potential issues. Ensuring a polished and flawless performance when time-to-market comes.
Whether a company chooses to use automated toolsets to self-manage EDI integration processes, such as new partner onboarding, or decide to have integration experts manage all of its EDI and B2B integration software processes, modern EDI software solutions should deliver both flexibility and scalability.
In-house EDI vs. Outsourced EDI
There are two methods to become EDI capable: In-house or outsourced. Now, to someone new to EDI or grappling with the choice, the question might be, “What’s the difference between in-house EDI and outsourced EDI?” Well, here’s a quick breakdown:
Read more : What To Serve With Cauliflower Steaks
In-house EDI requires:
- Hardware and/or software
- On-site staff/team with EDI knowledge and resources
- Available IT resources and support to maintain EDI capabilities and resolve issues
- Development and EDI mapping skills to onboard and update specific trading partners
- Internal integration competency
Outsourced EDI (AKA EDI-as-a-service):
- Requires no hardware and/or software
- The managed service provider performs all EDI-related processes, including development and mapping changes, allowing the organization to focus on business processes
- Cloud-based EDI frees up staff and IT departments to focus on other business-related items
- EDI Integration’s core competency is outsourced
EDI planning checklist
Choosing how to tackle the project of becoming EDI capable and/or modernized, whether it be in-house or outsourced, is no small task. It requires a strategic planning phase and an itemized tactical approach. Here’s a 12-step list to consider for effective EDI planning:
- Tally goals and constraints (requirements, improvements, budget, risks, etc.)
- Establish project infrastructure and policies
- Take inventory of legacy system(s) if applicable
- Perform gap analysis (based on current and anticipated use cases)
- Choose an EDI format capability and implementation model
- Identify additional resource needs
- Select a modern EDI solution software/hardware
- Staff personnel and define roles
- Train EDI and IT teams
- Choose a modernization strategy
- Define EDI interface and EDI integration architecture
- Establish a project schedule
As you consider your end-state for becoming EDI capable, make sure and create a visual representation of what that means. As a modernized EDI company, Cleo Integration Cloud delivers the right EDI tools to our customer base.
From left to right, comprehensive and automated EDI order processing should look something like this:
- Your retail, wholesale, or manufacturing partner begins an EDI process by sending an EDI 850 purchase order.
- Cleo Integration Cloud automatically checks that order for accuracy via EDI process automation
- Cleo Integration Cloud converts that EDI 850 into the necessary internal format your organization uses within your back-end ERP system.
- Cleo Integration Cloud ingests that internal format into the ERP using an API connection.
- The process is reversed for outgoing EDI documents: EDI 855, EDI 856, and EDI 810. Each of these transactions are sent in the required order to the trading partner as the good purchased becomes a good invoiced.
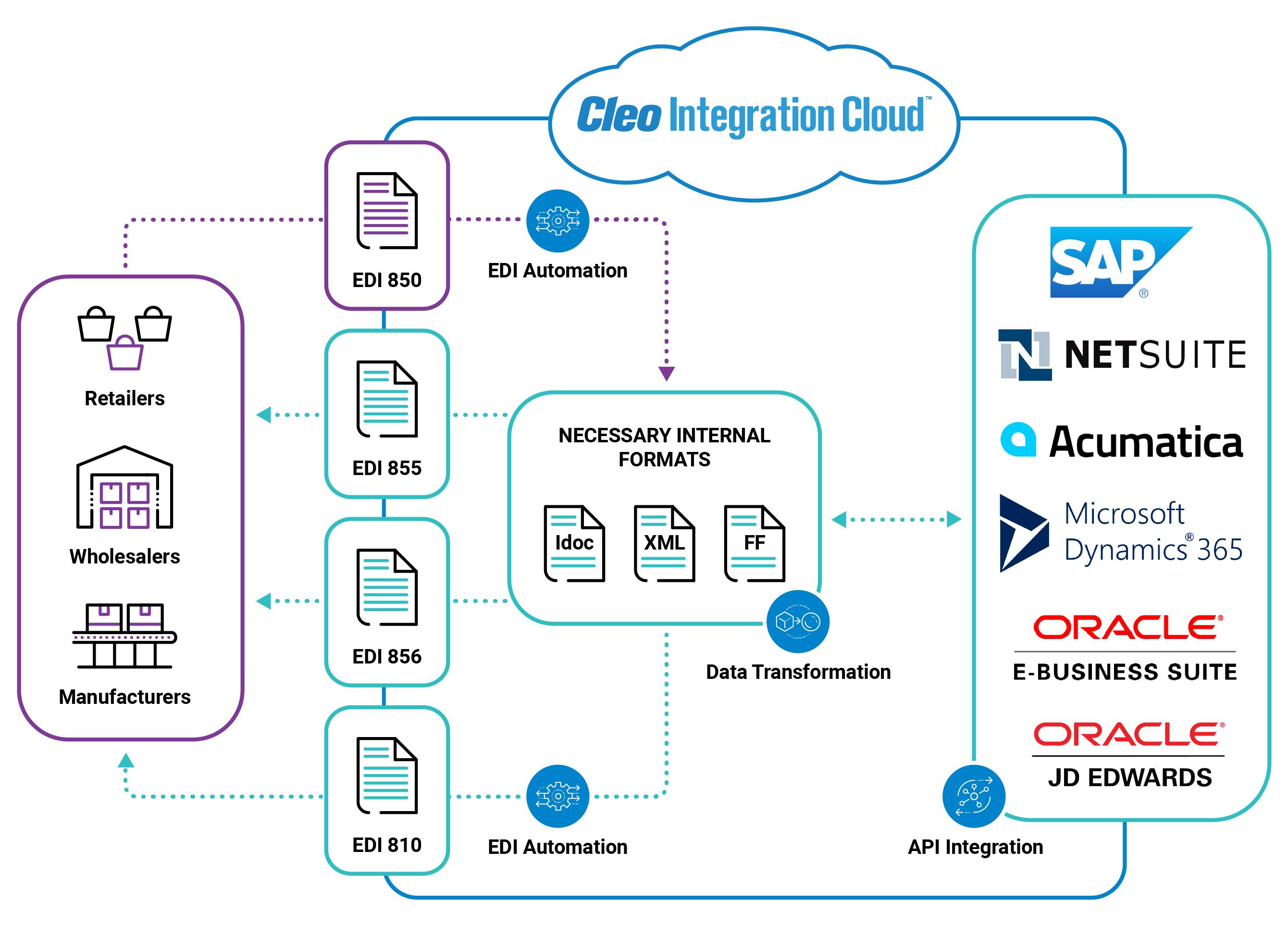
Of course, there are other things to consider: Prioritizing business connections; defining a phased migration approach from old to new solution; ensuring trading partner mandates; defining a plan to minimize business downtime; calculating manual processing costs vs. ROI of automation; determining the context within an overall business growth strategy; boosting partner service levels; reducing chargebacks/fees; integrating trading partners with limited technical capabilities; improving EDI visibility, audibility, and manageability; reducing service outage risks; consolidating infrastructure; addressing application and integration needs.
Did we mention becoming EDI capable is no small task? It might all seem overwhelming, but there are a silver lining and long-term payoff.
State-of-the-Art EDI Capabilities
There are key differences between traditional/legacy EDI and modern EDI solutions. One of the main differences is that modern EDI is highly efficient. This is because state-of-the-art EDI provides companies with end-to-end business process automation. This means that data is automatically exchanged in real-time between all necessary systems in a digital ecosystem. Real-time data exchanges ensure that processing is continually moving forward, and therefore minimizes any supply chain delays or disruptions.
Additionally, with modern EDI capabilities, companies can also better manage their supply chains and reduce costs by utilizing methods such as, vendor managed inventory (VMI), just-in-time (JIT), and just-in-sequence (JIS). By tapping into innovative supply chain management capabilities such as these, companies can garner greater control over their operations through improved supply chain visibility and business agility.
With improving supply chain agility, companies can expect an increase in revenue. According to our 2023 Global Supply Chain Executive Report, 49% of all respondents said their company gained $1 million or more in revenue from increased supply chain agility.
Overall, state-of-the-art EDI capabilities have the potential to increase a business’s efficiency, control, visibility, agility, and revenue.
Benefits of Becoming an EDI Capable Organization
For the most part, just about any company, large or small, can reap the benefits of EDI. Besides offering a standardized communication for common business document transactions (purchase orders (EDI 850), functional acknowledgments (EDI 997), freight receipts (EDI 310), payment order/remittance advice (EDI 820), and inventory inquiry (EDI 849)) that can streamline business workflows and onboard partners quickly, we know EDI solutions have the technology to deliver in five important ways: cost savings, speed, accuracy, efficiency, and security.
1. Cost savings
Quick fix: Reduce EDI transaction costs by 35 percent
The how and why: It all comes down to the bottom line, right? Increasing the worth of supply chain operations through real-time data insights leads to workflows that are predictable and controllable, both of which reduce customer costs. Then there are the savings on expenses that come along with paper and its maintenance (printing, reproduction, storage, filing, postage, and document retrieval). All those physical costs are greatly reduced or eliminated with EDI processes, lowering transaction costs by at least 35 percent. And with streamlined documentation, EDI compliance standards help avoid fines due to SLAs, payment delays, and performance gaps.
2. Speed
Quick fix: Cut processing times by 50 percent to 60 percent
The how and why: Automation through EDI speeds up every part of the business cycle. Comprehensive adoption of EDI that led to hands-free EDI order processing was shown to cut the order-to-shipment cycle by 50 to 60 percent. That in place of reliance on manually inputting data consumes valuable employee time and leads to a higher incidence of data errors. And this almost goes without saying, but there’s an enormous difference in transactions being exchanged in a manner of minutes rather than days or even weeks if there’s a reliance on postal service or other means of slow transfer.
3. Accuracy
Quick fix: Reduce errors by 40 percent
The how and why: Manually re-keying data into ERP and order systems are prone to inaccuracy and automation eliminates that problem and generates a 40 percent reduction in errors. EDI solutions also integrate with ERP systems to ensure transferable and accessible data is accurate and expectations are met with each transaction. As mentioned above, accuracy has a direct effect on a company’s bottom line with minimized chargebacks, delayed shipments, and incorrect product costs.
4. Efficiency
Read more : What Is Rebzyyx Gender
Quick fix: Process efficiency is a critical KPI for the business
The how and why: This is where fast and accurate processing combines to deliver true EDI integration and automation. Reduced hands-on processing means reduced manual data entry, fewer errors, and improved customer relationships, which can lead to improved delivery of goods and services and reduced customer turnover. Automated data exchanges among applications across the entire supply chain guarantee that B2B-critical documents and shipments are delivered promptly with real-time tracking visibility.
5. Security
Quick fix: Comply with industry and partner mandates
The how and why: EDI solutions are designed to ensure security with strict access to authorized users and equipped with archive tracking and audit trails. Data is shared securely across a wide variety of communications protocols and security standards, complying with mandates in global business today. And that assures transparency between business partners with electronic validations and receipts.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Different Levels and Considerations of EDI Capability
This blog provides valuable information about becoming EDI capable. However, as you navigate this decision, further questions might arise:
1. What are the different levels of EDI capability, and how do I determine the level necessary for my business needs?
EDI capability isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It exists on a spectrum, catering to varying business needs and trading partner requirements. Here’s how to navigate this:
- Basic EDI: Suitable for businesses with a limited number of trading partners and straightforward data exchange needs. This might involve exchanging invoices and purchase orders electronically.
- Intermediate EDI: Encompasses a wider range of functionalities, including additional document types, advanced mapping capabilities, and potentially integration with existing business systems. This caters to businesses with a moderate level of complexity in their data exchanges.
- Advanced EDI: Offers comprehensive capabilities for complex data exchanges, robust security features, and often integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This level suits businesses with extensive trading partner networks and diverse data exchange requirements.
Determining the optimal level for your business requires careful evaluation. Consider factors like:
- Trading partner requirements: Understand the EDI capabilities your key trading partners possess to ensure compatibility.
- Volume and complexity of data exchange: Assess the frequency and complexity of data you need to exchange with partners.
- Integration needs: Evaluate if integration with your existing business systems is necessary for efficient data flow.
By considering these aspects, you can choose the EDI capability level that aligns best with your specific business needs, whether you’re just getting started or an enterprise looking for a more robust solution.
2. What are the costs associated with becoming EDI capable, including software, implementation, and ongoing maintenance?
Becoming EDI capable involves upfront and ongoing costs:
- Software licensing: The cost of the EDI software itself varies depending on the chosen provider and the level of functionality required.
- Implementation services: Setting up and integrating the EDI system often requires professional assistance, which comes with associated costs.
- Ongoing maintenance: Maintaining the EDI system, including updates, security patches, and potential support services, incurs ongoing fees.
While the exact cost varies depending on your specific needs, understanding these cost components will help you budget effectively for your EDI implementation journey.
3. What are the long-term benefits and potential challenges of implementing EDI beyond the initial advantages mentioned in this article?
While EDI offers significant initial benefits like increased efficiency and accuracy, its impact extends beyond:
- Long-term cost savings: Streamlined processes and reduced manual intervention can lead to cost savings over time.
- Improved collaboration: EDI facilitates closer relationships with trading partners through efficient and reliable communication.
- Enhanced scalability: An EDI system can adapt and grow alongside your business, accommodating future expansion and evolving data exchange needs.
However, implementing EDI also presents potential challenges:
- Change management: Adapting to a new system and workflows might require employee training and support to ensure smooth adoption.
- Security considerations: Maintaining robust security measures is crucial to protect sensitive data exchanged electronically.
- Technical expertise: Depending on the chosen level of complexity, ongoing technical expertise might be needed to manage and maintain the EDI system.
By acknowledging both the long-term benefits and potential challenges, you can make an informed decision about EDI implementation and develop strategies to maximize its success within your unique business context.
Remember, becoming EDI capable is a strategic decision with both advantages and considerations. Understanding the different levels, associated costs, and long-term implications empowers you to make an informed choice and leverage the full potential of EDI for your business success.
Manage Your Transactions Better
When it comes down to it, EDI is impossible to avoid. For any business that relies on any part of the supply chain, that is not a bad thing. EDI is a technology that can be delivered to facilitate connectivity and integration across complex business trading environments. Consider the impact of being able to seamlessly conduct business digitally even with multi-cloud and multi-vendor integration requirements. So, if a company isn’t EDI capable, the harsh reality is that it won’t be business capable either. Once an organization successfully implements or modernizes its EDI capabilities for automated workflows, it will become more flexible, more scalable, more efficient, more transparent, and easier to do business with.
Contact us Today to Become EDI Capable
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHAT

