Celtic salt or Celtic sea salt, also commonly known as sel gris (gray salt) in French, is harvested from seawater in the estuaries near the town of Guérande in France. Sel gris is a coarse salt that is typically harvested with a moisture content of 15%, whereas most sea salts and commercially manufactured salt maintain moisture contents of less than 1%.
As the tide comes in, seawater is first allowed to settle in clay silt ponds where the combined effects of wind and sun form a dense brine. The brine is then channeled to shallow salt pans dug in the native clay where it crystallizes via solar evaporation to form salt crystals. The clay from the silt as well as from the salt pans impart sel gris with its characteristic gray color.
You are viewing: Where Is Celtic Sea Salt From
Is Celtic Salt Different from Other Sea Salts?
Yes, it’s somewhat different because of the mineral contributions of the clay it is harvested near. But I know of no comprehensive, modern analysis of Celtic salt, so it is difficult to determine if the harvesting of sea salt from the estuaries near Guérande affects the salt concentrations normally found in seawater. From a chemical perspective, there is no reason to expect that the relative concentrations of the dissolved elements normally found in seawater would be altered, unless the processing of sel gris adds or subtracts elements.
The salts in seawater are stable chemical compounds whose relative percentages are invariant.1,2 The absolute weights of each of seawater’s dissolved salts will vary depending only upon the amount of moisture that is retained in sel gris at harvest. Because Celtic sea salt is typically harvested with a 15% moisture content, then the absolute weight of the dissolved salts will be about 85% of their equivalent amount in dry sea salt (<1 % moisture).
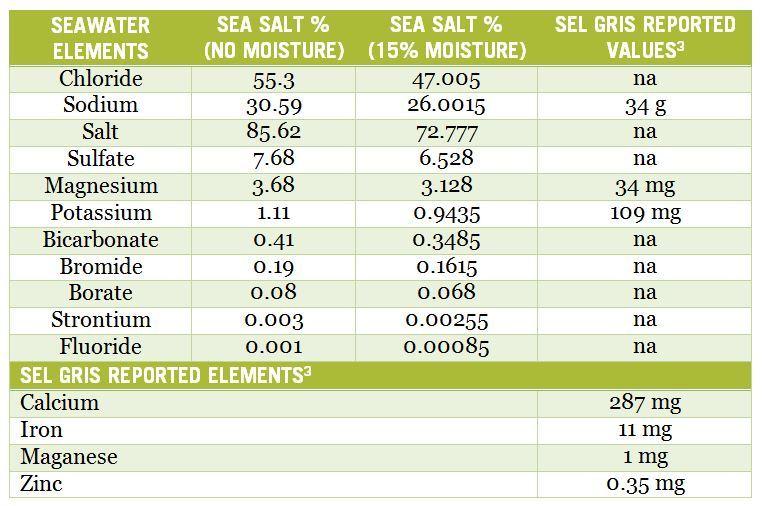
In the single account3 I am aware of, the following concentrations of dissolved salts were reported for sel gris (100 grams):
- Sodium 34g
- Calcium 287mg
- Potassium 109mg
- Magnesium 34mg
- Iron 11mg
- Manganese 1mg
- Zinc 0.35mg
Read more : Where Are My Scanned Documents
Let’s take a look at these values and contrast them to normal dry (no moisture) sea salt or normal sea salt containing 15% moisture which is similar to Celtic salt’s moisture content in the table below.
We should first address a few important points:
- Does the data reported for sel gris appear to be accurate?
- Is it possible that the addition of clay to Celtic sea salt increases its concentration of some minerals?
- Is it possible that evaporation of sea salt in clay pans could reduce the relative concentration of normal sea salts?
- Is sel gris healthy and should it be a part of contemporary Paleo diets?
What Kind of Clay Is in Celtic Sea Salt?
To answer these questions we first must take a quick look at the minerals normally found in clays.4 Geologists have classified clay minerals into four groups:
- Kaolinite
- Illite
- Smectite
- Vermiculite
All clays are rich in iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg).4 The principal cations in illites are potassium (K), calcium (Ca) and Mg; in smectites they are Ca, sodium (Na), Mg, Fe, Manganese (Mn) and zinc (Zn); in vermiculites the principle cation is Mg, but these compounds also contains significant quantities of Fe and Na.
Accordingly, sea salts contaminated with residual clays during harvest might be expected to contain additional amounts of Na, Ca, Mg, Fe, Mn, Zn and/or K.
Does Celtic Salt Have More Magnesium and Potassium?
Read more : Where Does Jenelle Evans Live
Although some clays contain significant amounts of magnesium and potassium, the data above actually demonstrate Celtic salt to maintain lower concentrations of both of these elements than normal sea salt.
Regular sea salt represents a physiologically insignificant source of Ca and Fe, whereas the reported values for the reported sel gris data are considerably higher.
Whether these data are accurate or represent measurement errors is unknown. Although consumption of 100 grams of Celtic sea salt delivers moderate quantities of Ca (287 mg) and Fe (11 mg), it does so at a terrible nutritional cost in terms of salt ingestion. Those 100 grams of sel gris using reported data translates to 34 grams or 3,400mg of sodium. The United States Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommends that we limit our sodium consumption to no more than 2,300mg per day.5
Celtic Salt Is Actually Worse for You Than Table Salt
Indeed, if the reported sel gris data is accurate, then the spreadsheet above confirms that Celtic sea salt contains nearly 31% more salt (both sodium and chloride) than normal salt derived from seawater, making it even less healthy than traditional table salt!
On paper, it may appear that Celtic salt slightly more nutrient dense for a select few minerals than normal sea salt, but the bottom line is that sel gris, sea salt, and common table salt all have undesirably high concentrations of NaCl (sodium chloride) which promote hypertension, osteoporosis, kidney stones, Ménière’s disease (ear ringing), insomnia, motion sickness, asthma, and a variety of cancers.
Salt, be it in the form of sel gris, sea salt or plain commercial salt, is definitely not Paleo because these high quantities of sodium would have been infrequently encountered in our history.
References
- Castro P, Huber M. Marine Biology, McGraw-Hill, 9th Ed., New York, NY, 2012.
- Baseggio G. 1974. The composition of seawater and its concentrates. Proc. 4th Int. Symp. Salt Vol. 2, pp. 351-358. Northern Ohio Geological Society, Inc., Cleveland, OH.
- Bitterman, M. Salted: A Manifesto On The World’s Most Essential Mineral With Recipes. Ten Speed Press, New York, 2010.
- //earth.usc.edu/~dfarris/Mineralogy/17_ClayMinerals.pdf
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vital signs: food categories contributing the most to sodium consumption – United States, 2007 – 2008, February 7, 2012.
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHERE
