Reversible And Irreversible Acid-Base Reactions
Last time we learned about pKa and how it’s the closest thing we have to a universal measurement of the strengths of all kinds of different acids and bases.
You are viewing: Which Acid Base Chemical Reaction Is Irreversible
I also referred to a post on how to use a pKa table (key lesson: stronger acid plus stronger base gives weaker acid and weaker base).
We can use pKa to estimate the equilibrium constants for acid-base reactions.
A handy rule of thumb for an acid-base reaction is that if the acid and the conjugate acid are separated by more than 10 pKa units, the reaction is essentially irreversible.
Table of Contents
- An Irreversible Acid-Base Reaction: Strong Acid (HCl) Plus Strong Base (NaOH) Giving Water
- An Easily Reversible Acid-Base Reaction: Methanol (pKa 15.2) With Water (pKa 14)
- At What Point Does An Acid-Base Reaction Become Irreversible For Practical Purposes?
- Application: In The Claisen Condensation, The Starting Ester Is Less Acidic Than CH3OH By About 10 pKa Units
- Notes
1. An Irreversible Acid-Base Reaction: Strong Acid (HCl) Plus Strong Base (NaOH) Giving Water
On one extreme, we have one mole of a really strong acid – let’s say hydrochloric aid (HCl), pKa -8. And to it, we add (slowly!) a solution of water containing one mole of sodium hydroxide (the conjugate base of water, pKa 14).
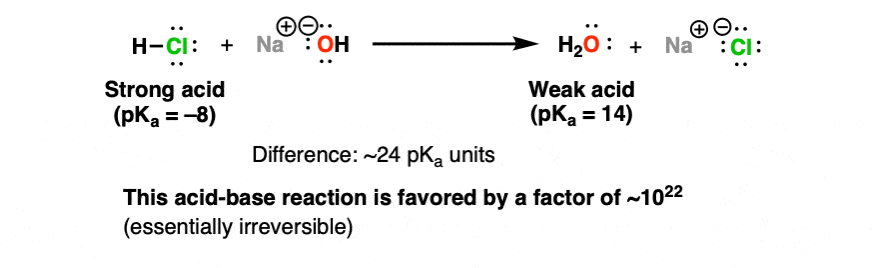
HCl and NaOH react to give water and NaCl . How favorable is this reaction? We can make a rough estimate. The pKa of HCl is -8. Sodium hydroxide is the conjugate base of H2O (pKa 14).
That’s a difference of about 22 pKa units – and since each pKa unit represents one order of magnitude, this reaction is favorable with an equilibrium constant of about 10 to the power of 22.
For all intents and purposes, a reaction with an equilibrium constant this huge is irreversible.
That is to say that HCl and NaOH are completely consumed when they react together, giving only H2O and NaCl.
2. An Easily Reversible Acid-Base Reaction: Methanol (pKa 15.2) With Water (pKa 14)
Read more : Which Statement Correctly Identifies The Loan Type With Its Function
What about the other extreme: the reaction of methanol (pKa of 15.2) with sodium hydroxide (the conjugate base of water, pKa 14)?
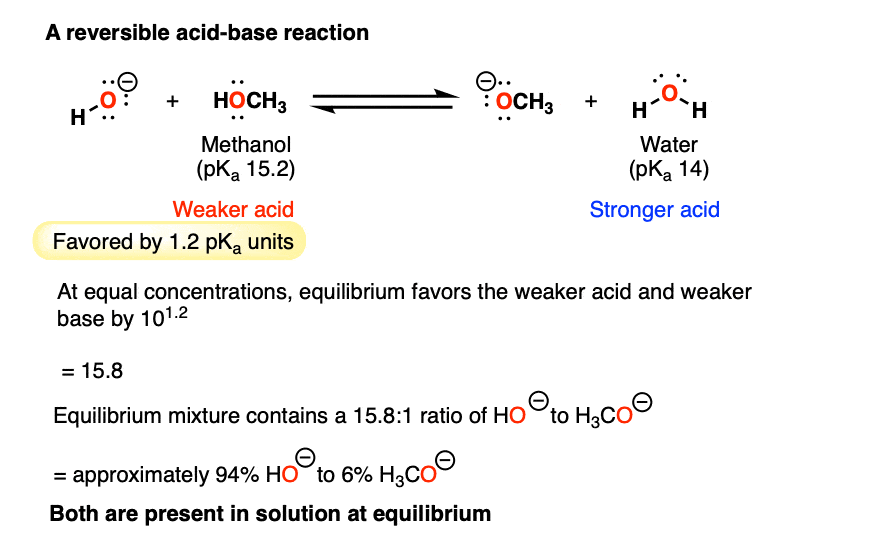
Neither side of the acid-base reaction is strongly favored. Here we’re dealing with a very small difference in pKa – only 1.2 pKa units.
So the equilibrium constant here would only be about 10 to the power of 1.2 —> 15.8 toward giving the weaker acid (CH3OH) and the weaker base HO(-).
At equilibrium we’d expect to have a mixture of about 94% HO(-) [the weaker base] and 6% H3CO(-) [the stronger base].
In other words, both species are present in solution.
3. At What Point Does An Acid-Base Reaction Become Irreversible For Practical Purposes?
So how far can we stretch this? In between these two extremes, at what point does a reaction become irreversible for practical purposes?
There’s no hard and fast rule on this. But for practical purposes, a good rule of thumb is about 10 pKa units.
That is to say, if the difference in pKa‘s between an acid and a base (actually, the conjugate acid of the base) is about 10 pKa units or less, it is useful to consider their acid-base reaction to be in equilibrium.
Think about what that means – a ratio of one molecule in 10 billion can make the difference in a reaction!
One in 10 billion might not sound like a lot. But when you consider that a mole contains 10 to the power of 23 molecules, and each of them are colliding millions of times per second, the odds aren’t really as bad as they look.
f your only chance of buying a private jet rested on you winning a Powerball lottery – but you were able to fill out hundreds of thousands of entries per second, every second, you’d be at the G5 dealer by next Tuesday.
Read more : Which State Has The Most Incest
Here’s an example you’ll see in Org 2. The Claisen condensation begins with the deprotonation of an ester (pKa ~24) by an alkoxide ion (conjugate base of an alcohol, pKa ~15). (See article:The Claisen Condensation)
That’s disfavored by about 10 to the power of 9, since we’re going from a weaker base (alkoxide) to a stronger base (deprotonated ester, a.k.a ester enolate).
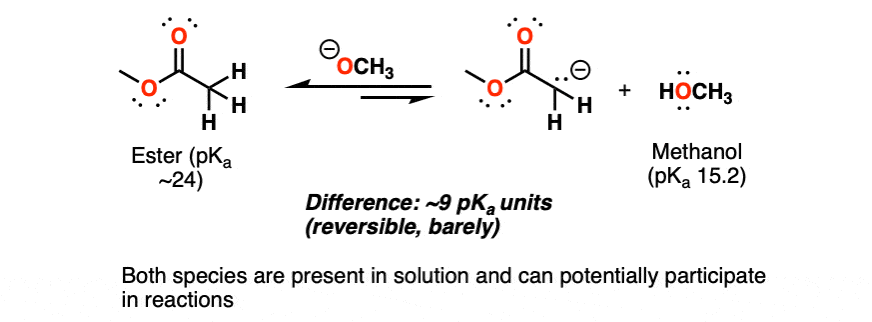
Even though there’s only a small amount of the deprotonated ester present at equilibrium, this can be enough to get the reaction to go! You can take my word for it – that this rule of thumb applies – and leave it there.
Or if you’d prefer to go through an actual application of this concept, I’ll finish up with that.
4. Application: In The Claisen Condensation, The Starting Ester Is Less Acidic Than CH3OH By About 10 pKa Units
One application of this concept can be found in the Claisen condensation of esters. The Claisen condensation involves the addition of a deprotonated ester (an “enolate”) to another equivalent of an ester, through an addition-elimination reaction (see article: The Claisen Condensation)
The first step is deprotonation of the ester by an alkoxide ion [in this case CH3O(-) ] as mentioned above. This enolate can then attack a second equivalent of ester, which then eliminates an equivalent of alkoxide ion.
This reaction is also potentially reversible. However, the protons of the new product – a “beta-keto ester” – are considerably more acidic than those of the starting ester, and an acid-base reaction between it (pKa 12) and alkoxide (pKa 15) is quite favorable.
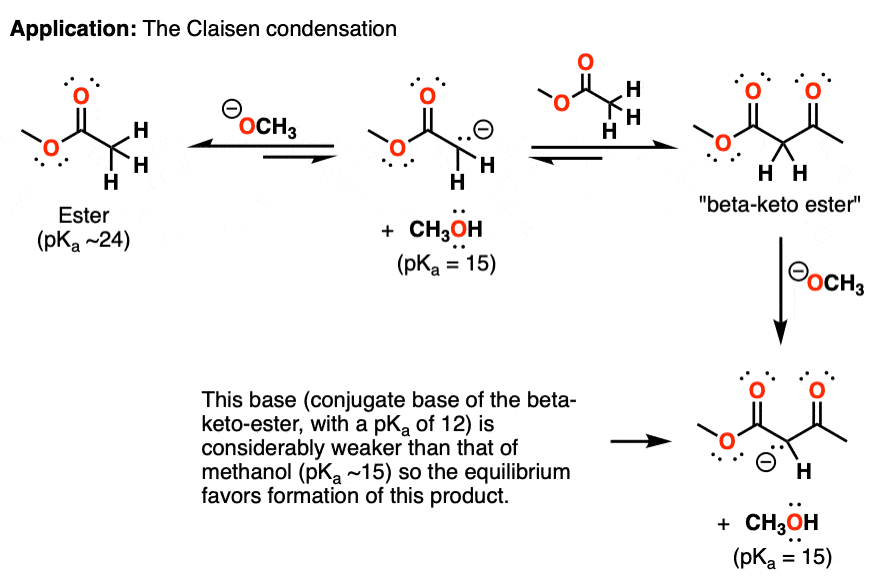
The equilibrium eventually favors the final product, because the conjugate base of the beta-keto ester (pKa 12) is considerably weaker than methanol (pKa ~15).
In other words, even though the first step is extremely disfavored, this is made up for by the fact that there is a very good “driving force” for the subsequent reaction.
Next Post: Acid-Base Reactions Are Fast
Notes
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH
