Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are an essential tool for businesses looking to streamline their operations and improve efficiency. These integrated systems enable businesses to manage and harmonize various aspects of their operations, from procurement and human resources to customer service and finance, within a single platform. The aim is to facilitate seamless data sharing and cooperation between different departments, ultimately leading to increased productivity and profitability.
Among the various functionalities of ERP systems, financial management stands out as particularly critical. ERP financial management systems contain modules for accounting, budgeting, risk management, and more, providing companies with a comprehensive overview of their financial health. Without an ERP financial management system, companies may struggle to keep track of their financial transactions, potentially leading to errors and inefficiencies. This could also affect strategic decision-making, as companies lack the real-time financial data needed to make informed decisions.
You are viewing: Which Activities Do Accounting And Finance Components Perform
What Is ERP Finance?
ERP Finance, or Enterprise Resource Planning Finance, is a crucial component of ERP systems. It refers to the suite of applications within an ERP system that manages and integrates all the financial information of a business. This system collects, stores, manages and interprets data related to various financial activities including accounting, budgeting, cash flow management, accounts payable and receivable, asset management, and more. By providing a single, unified view of all financial data, ERP Finance allows companies to streamline their financial operations, improve financial reporting accuracy, enhance compliance with financial regulations, and support strategic decision-making based on real-time financial insights.
ERP Finance vs. Accounting Solution
While both ERP Finance and standalone accounting solutions handle financial data, they differ significantly in scope and integration capabilities. An accounting solution is primarily designed to record and process accounting transactions within functional areas such as accounts payable, accounts receivable, and payroll. It’s a specialized tool focused solely on managing the financial transactions of the business.
On the other hand, ERP Finance is a comprehensive system that not only includes accounting functionalities but also integrates these functionalities with other business operations. It provides a unified platform that allows for seamless data flow between various business departments, ensuring that financial data is consistent across the organization. This integration makes ERP Finance a more robust tool for strategic decision-making, as it provides real-time financial insights that take into account the overall operations of the business.
Key Features of ERP Finance
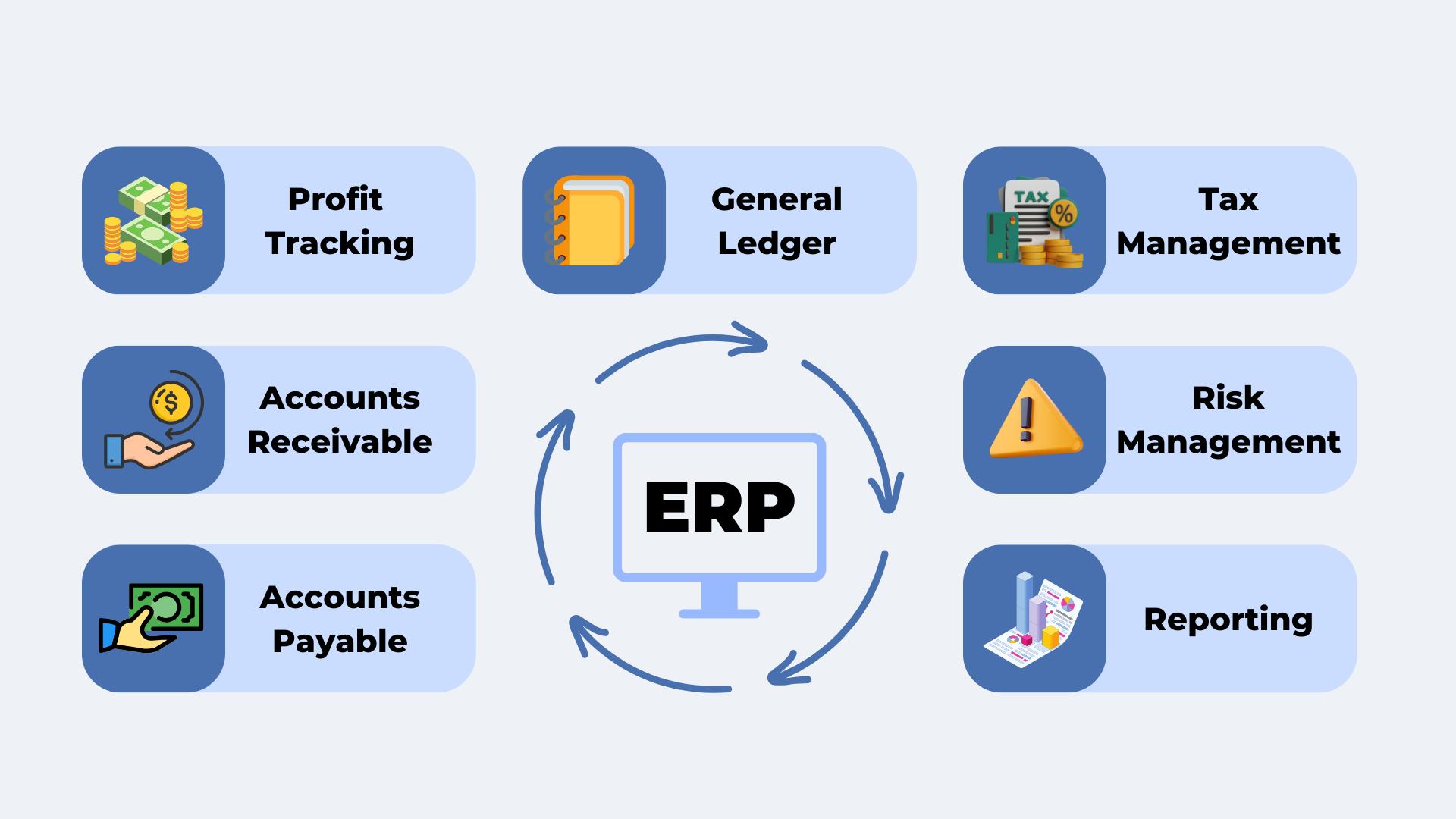
1/ Profit Tracking
Profit tracking is a fundamental feature of ERP Finance systems, allowing businesses to monitor their profitability in real-time. The system meticulously logs all income and expenses, automatically calculating net profit and offering a clear view of the financial health of the company. This feature is especially valuable for businesses dealing with multi-currency transactions, as it can convert and consolidate financial data into a single currency for more straightforward profit assessment. Furthermore, it enables businesses to track profit on a granular level, such as by product, by project, or by department, providing valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Moreover, the profit tracking feature is customizable, enabling businesses to define their parameters based on their specific needs. For instance, a company can set up the system to track profit margins based on various factors such as product type, customer segment, or geographical market. This level of tracking can yield comprehensive insights into where exactly profits are being generated, thereby helping identify the most profitable areas of the business and those that need improvement. Additionally, with real-time profit tracking, businesses can quickly respond to any changes in profitability, making necessary adjustments to maintain financial equilibrium.
2/ General Ledger
Read more : Which Of The Following Statements About Unconscious Bias Is True
The General Ledger in an ERP Finance system is essentially the backbone of any financial management system. It serves as a central repository for collecting and organizing all the company’s financial transactions. This feature records debit and credit entries (transactions) across all accounts and departments, ensuring that every financial transaction is tracked and categorized correctly. It provides a consolidated view of financial data, enabling the company to maintain a comprehensive, chronological record of its financial activities.
The General Ledger feature also supports the generation of financial reports, such as balance sheets and income statements, contributing to improved financial transparency and decision-making. Such an integrated and unified view of financial data helps business leaders make informed financial and strategic decisions, backed by real-time, accurate data.
3/ Tax Management
The Tax Management module of an ERP Finance system is a pivotal feature that helps businesses handle their complex tax obligations efficiently. It automatically calculates, deducts, and files various taxes based on the geographical location and the nature of the transaction, ensuring compliance with local, state, and federal tax regulations.
This feature covers a broad range of taxes, including sales tax, value-added tax (VAT), and corporate tax, among others. Moreover, the Tax Management module also facilitates the preparation and filing of tax returns, reducing the risk of errors or omissions that could lead to penalties or fines. By automating these tax-related processes, businesses can ensure accuracy, save time, and focus better on their core operations.
4/ Accounts Receivable
The Accounts Receivable (AR) module in an ERP Finance system plays an important role in managing money owed by customers. It automates and streamlines the process of invoicing and collecting payments from customers, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. The AR module records all sales transactions that are not paid immediately, tracking the amounts and dates of upcoming payments. This aids in the preparation of cash flow forecasts and ensuring timely collection of revenue.
Additionally, the module can generate aging reports, providing insights into unpaid customer invoices and helping identify issues that may require attention. By automating these processes, the AR module in ERP Finance system improves cash flow management, reduces the risk of errors, and enhances customer relationships by ensuring a more consistent, professional approach to collection activities.
5/ Accounts Payable
The Accounts Payable (AP) feature in an ERP Finance system is integral to managing the company’s financial obligations. It meticulously tracks all unpaid invoices, allowing businesses to stay on top of what they owe to suppliers or vendors. The AP module automates the entire payment process, from invoice receipt and approval to payment issuance, thereby improving accuracy and efficiency. Besides, it helps businesses avoid late payment penalties and maintain good relationships with their suppliers by ensuring payments are made timely and accurately.
Read more : Which Of The Following Exemplifies Extrinsically Motivated Behavior
6/ Risk Management
The Risk Management feature in ERP Finance systems is a component designed to identify, assess, and strategize processes to mitigate business risks. This feature provides tools for tracking and evaluating potential financial risks associated with various business operations, such as fluctuations in market conditions, compliance failures, or potential fraud. This allows businesses to proactively manage these risks, devise strategies to mitigate their impact, and make informed decisions. The Risk Management module also facilitates reporting and visualization of risk patterns, enabling organizations to foresee and address potential issues, hence fostering a resilient and risk-aware culture.
7/ Reporting
The Reporting feature of an ERP Financial Management system is also necessary for financial analysis, forecasting, and decision-making. This feature enables companies to generate a variety of financial reports, including balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements, and more, using real-time data from various modules of the system.
With customizable reporting options, the user can tailor reports based on specific parameters, such as department, time period, project, or product, providing a detailed and granular view of the company’s financial status.
Moreover, these reports can be created and accessed in a user-friendly format, enhancing readability and interpretation of financial data. This feature not only saves time but also ensures accuracy and consistency in reporting, thereby supporting informed business decisions and strategic planning.
ERP Finance: Who Needs It?
ERP Finance systems are indispensable tools for businesses of all sizes and across industry verticals. They are particularly beneficial for businesses aiming to streamline their financial operations, improve accuracy, and make data-driven business decisions. With an ERP Finance system, organizations can automate tedious manual tasks, reduce the risk of human errors, and increase the efficiency of their financial operations. This leads to cost savings, improved productivity, and allows the finance team to focus on more strategic tasks.
The first category of businesses that could significantly benefit from ERP Finance systems are those with complex financial operations, such as multinational corporations. These organizations need to manage multiple currencies, adhere to various tax regulations, consolidate financial data from numerous departments and regions, and generate comprehensive financial reports. ERP Finance systems are designed to handle these complexities, making them a perfect fit for these organizations.
Secondly, fast-growing startups and SMEs would find ERP Finance systems extremely beneficial. As these businesses expand, their financial transactions increase, become more complex, and are prone to errors if managed manually. An ERP Finance system provides the much-needed scalability to support their growth, enabling them to manage increased financial transactions with the same efficiency and accuracy.
Lastly, businesses that operate in highly regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing may find ERP Finance systems particularly useful. These systems ensure compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties. Moreover, they provide audit trails, ensuring transparency and traceability of all financial transactions, which is critical in these industries.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, an ERP Finance system is a crucial tool that modern businesses should consider incorporating into their operations. Its ability to automate complex financial tasks, ensure accuracy, and provide detailed, custom reports makes it an invaluable asset, particularly for organizations with intricate financial operations, rapidly growing SMEs, and businesses in highly regulated industries. Adopting an ERP Finance system is a strategic decision that can drive efficiency, promote transparency, and support informed decision-making, positioning businesses for long-term success.
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH
