Valence electrons are the s and p electrons in the outermost shell. The electrons present in the inner shell are core electrons. When we study and observe the atom of an element, we come across tiny subatomic particles called valence electrons. Lewis structures help us to track the valence electrons and predict the types of bond.
Valence electrons are all arranged in different orbitals or shells and are mostly negatively charged particles. Further, these electrons are responsible for interaction between atoms and the formation of chemical bonds. However, not all electrons are associated with the atom. Only the electrons present in the outermost shell can participate in the formation of a chemical bond or a molecule. Such type of electrons is called valence electrons.
You are viewing: Which Characteristic Do Valence Electrons Indicate About Reactions Between Atoms
Table of Contents
- What are Valence Electrons?
- Related Videos
- Characteristics of Valence Electron
- Determination of Valence Electrons
- Valence Electron of Elements
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What are Valence Electrons?
Valence is the number of electrons an atom must lose or gain to attain the nearest noble gas or inert gas electronic configuration. “Electrons in the outer shells that are not filled are called valence electrons”.
The valence electrons are part of the chemical reactions because they contain more energy compared to the electrons present in inner orbits. Meanwhile, the number of valence electrons present also helps us determine a specific element’s chemical properties, such as its valence or valency, the formation of bonds with other elements. It also gives us an idea of how readily the atoms can form bonds, the number of unpaired electrons and how many atoms can take part.
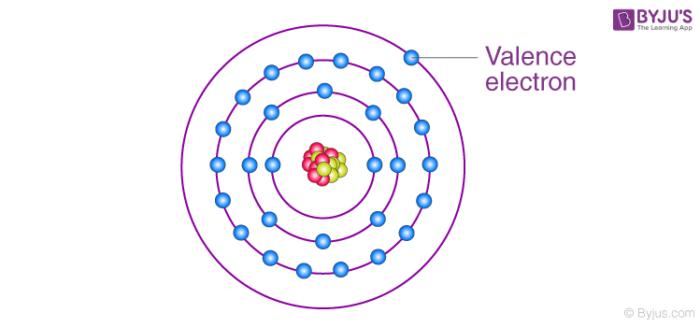
Related Videos
Characteristics of Valence Electron
Electrons are involved in the chemical bonding and reactions of the atom. It is said to occupy orbitals in an atom. The number of valence electrons of an atom can be obtained from the periodic table because it is equal to the group number of the atom. Atoms are most stable if they have a filled valence shell of electrons. Atoms transfer or share electrons in such a way that they can attain a filled shell of electrons.
Some key characteristics of a valence electron are;
- For the main group elements, the valence electron exists only in the outermost electron shell.
- A valence electron can exist in the inner shell of a transition metal.
- An atom consisting of a closed shell of valence electrons will usually be chemically inert.
- A valence electron can either absorb or release energy in the form of a photon.
- Valence electrons also determine the electrical conductivity of an element. Depending on the nature of elements can be metal, non-metal, or metalloid.
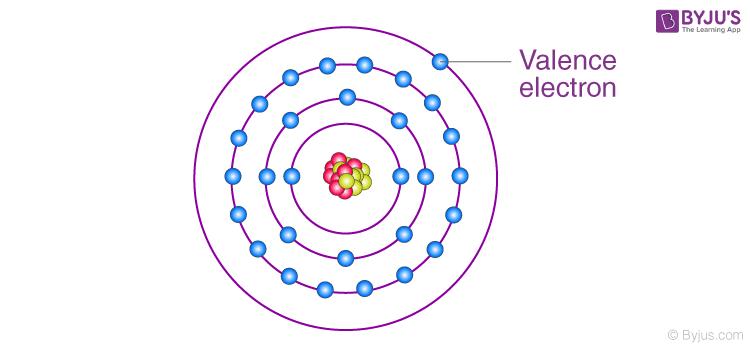
Determination of Valence Electrons
One of the easiest ways to find valence electrons is by checking out the elements’ place in the periodic table. The valence electrons of an element can be found by closely examining the vertical column in which the elements are grouped. By looking at the group number that is given we can identify the number of valence electrons that an element which is listed under that specific column has.
Read more : Which Thunderbolt Do I Have
Another way to find or determine valence electrons is by knowing the electronic configuration.
However, if we take the transition metals (groups 3-12), finding the valence electron is quite complicated. These elements’ atomic structure is rigid and the d subshell is incomplete and sits lower than the outer shell.
Valence Electron of Elements
Here is a list of the number of valence electrons present in the different groups.
Periodic Table Group Valence Electrons Alkali metals – Group 1 (I) 1 Alkaline earth metals – Group 2 (II) 2 Boron group – Group 13 (III) 3 Carbon group – Group 14 (IV) 4 Nitrogen group – Group 15 (V) 5 Oxygen group – Group 16 (VI) 6 Halogens – Group 17 (VII) 7 Noble gases – Group 18 (VIII or 0) 8
To learn more about this topic and other related topics, register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH
