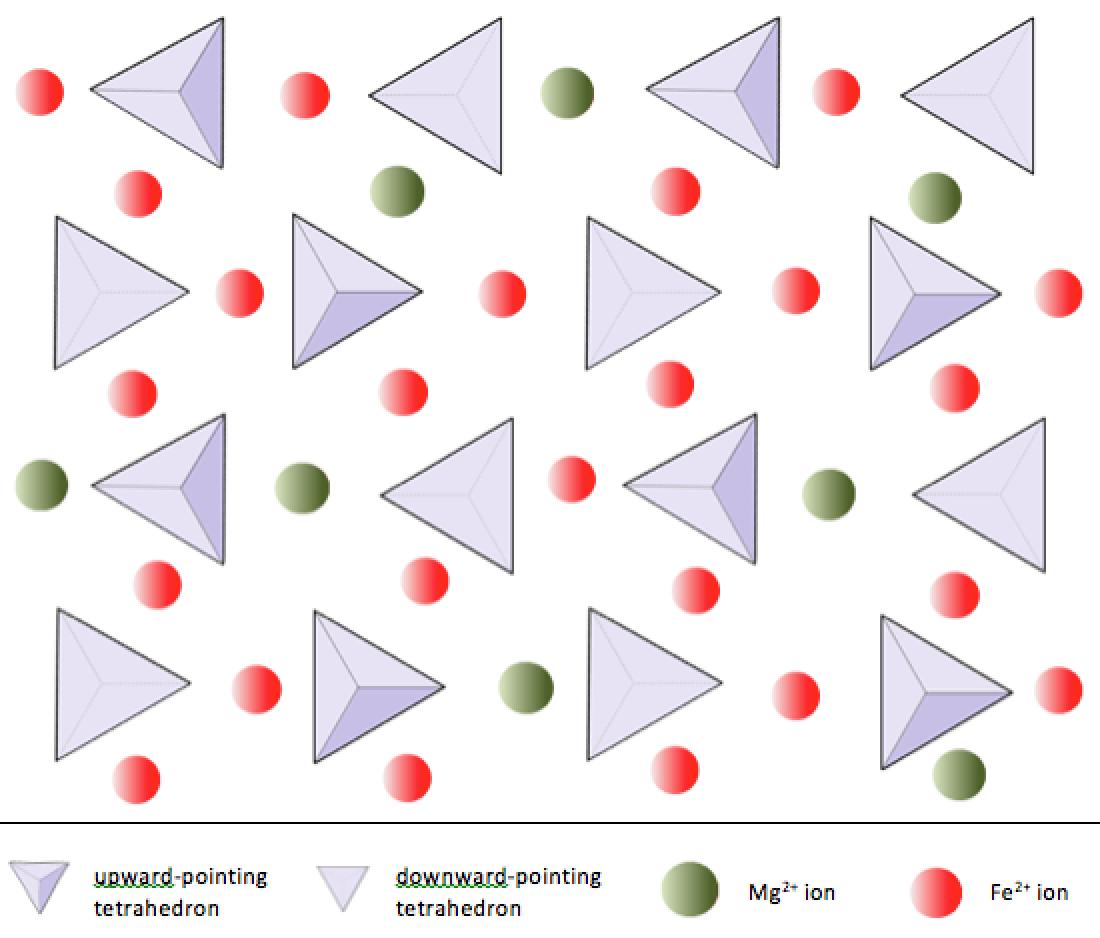
In olivine, unlike most other silicate minerals, the silica tetrahedra are not bonded to each other. They are, however, bonded to the iron and/or magnesium as shown on Figure 2.10.
- Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Abdominal Trauma Is Correct
- The Best Harry Potter Books: A Personal Ranking
- Which Of The Following Are Characteristics Of Mass Communication
- Which Statements Describe Phase Changes Check All That Apply
- Which Surchargeable Events Count Toward Possible License Suspension
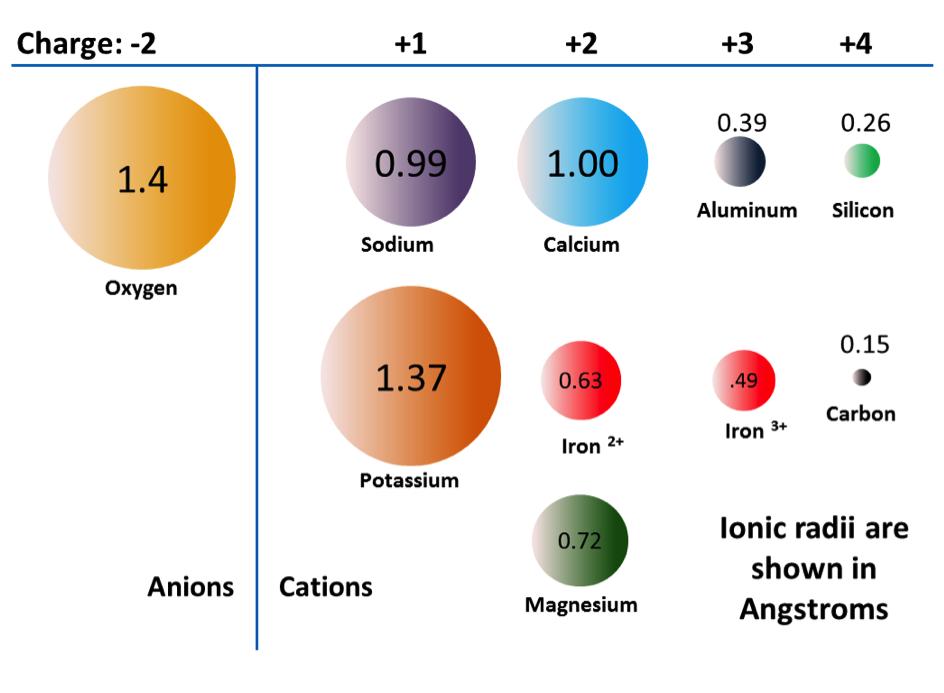
As already noted, the +2 ions of iron and magnesium are similar in size (although not quite the same). This allows them to substitute for each other in some silicate minerals. In fact, the common ions in silicate minerals have a wide range of sizes, as shown in Figure 2.11. All of the ions shown are cations, except for oxygen. Note that iron can exist as both a +2 ion (if it loses two electrons during ionization) or a +3 ion (if it loses three). Fe2+ is known as ferrous iron. Fe3+ is known as ferric iron. Ionic radii are critical to the composition of silicate minerals, so we’ll be referring to this diagram again.
You are viewing: Which Is Not A Type Of Silicate Structure
The structure of the single-chain silicate pyroxene is shown on Figures 2.12 and 2.13. In pyroxene, silica tetrahedra are linked together in a single chain, where one oxygen ion from each tetrahedron is shared with the adjacent tetrahedron, hence there are fewer oxygens in the structure. The result is that the oxygen-to-silicon ratio is lower than in olivine (3:1 instead of 4:1), and the net charge per silicon atom is less (-2 instead of -4), since fewer cations are necessary to balance that charge. Pyroxene compositions are of the type MgSiO3, FeSiO3, and CaSiO3, or some combination of these. Pyroxene can also be written as (Mg,Fe,Ca)SiO3, where the elements in the brackets can be present in any proportion. In other words, pyroxene has one cation for each silica tetrahedron (e.g., MgSiO3) while olivine has two (e.g., Mg2SiO4). Because each silicon ion is +4 and each oxygen ion is -2, the three oxygens (-6) and the one silicon (+4) give a net charge of -2 for the single chain of silica tetrahedra. In pyroxene, the one divalent cation (2+) per tetrahedron balances that -2 charge. In olivine, it takes two divalent cations to balance the -4 charge of an isolated tetrahedron.
Read more : Which Protein Domains Contain The Four Mc1r Missense Mutations
The structure of pyroxene is more “permissive” than that of olivine — meaning that cations with a wider range of ionic radii can fit into it. That’s why pyroxenes can have iron (radius 0.63 Å) or magnesium (radius 0.72 Å) or calcium (radius 1.00 Å) cations.
In amphibole structures, the silica tetrahedra are linked in a double chain that has an oxygen-to-silicon ratio lower than that of pyroxene, and hence still fewer cations are necessary to balance the charge. Amphibole is even more permissive than pyroxene and its compositions can be very complex. Hornblende, for example, can include sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, aluminum, silicon, oxygen, fluorine, and the hydroxyl ion (OH-).
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH
