What are Free Radicals?
A free radical is termed as a molecular species which can contain an unpaired electron in its atomic orbital and can exist independently.
All the radicals share some common properties due to the unpaired electron.
You are viewing: Which Molecule Would You Expect To Be A Free Radical
Generally, molecules bear bonding electron pairs and lone pairs a nonbonding electron pair or un-shared electron pair. Each bonding or nonbonding electron pair has two electrons which are in opposite in spin orientation, +1/2 and -1/2 in one orbital based on Pauli’s exclusion principle, whereas an unpaired electron is a single electron, alone in one orbital. A molecule that has an unpaired electron is called a free radical and is a paramagnetic species.
Table of Contents
-
- Properties of Free Radicals
- Examples of Free Radicals
- Types of Free Radicals
- Uses of Free Radicals
- Sources of Free Radicals
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQ
Properties of Free Radicals
-
-
-
- Free radicals are unique and rare species and are present only under special and limited conditions. However, some free radicals are familiar to us in our lives.
- Molecular oxygen is a typical free radical, a bi-radical species. Standard and stable molecular oxygen is in triplet state and the two unpaired electrons have the same spin orientation in two orbitals, respectively, having the same orbital energy based on Hund’s rule.
- Nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide are also stable, free radical species. Moreover, the reactive species involved in immunity are oxygen free radicals, such as superoxide anion radical and singlet molecular oxygen.
- So free radicals are very familiar to us in our lives and are very important chemicals.
- Free radicals are highly reactive and very unstable. They can donate an electron or accept an electron from other molecules, therefore, can behave as oxidants or reductants.
-
-
Examples of Free Radicals
Consider three reactive species: a methyl anion, methyl cation and methyl radical. These radicals are shown below.
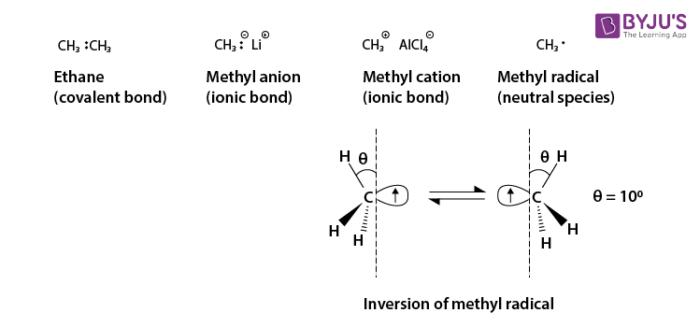
Ethane is composed of two methyl groups connected by a covalent bond and is a very stable compound. The methyl anion and methyl cation have an ionic bond mainly between carbons and counter ions respectively and are not particularly unstable though there are some rather moisture sensitive species.
However, the methyl radical is an extremely unstable and reactive species because its octet rule on the carbon is not satisfied. The carbon atom in the methyl cation adopts sp2 hybridization and the structure is triangular and planar. The carbon atom in the methyl anion adopts sp3 hybridization and the structure is tetrahedral, However the carbon atom in the methyl radical adopts a middle structure between the methyl cation and the methyl anion, and its pyramidal inversion rapidly occurs even at extremely low temperatures.
The most important free radical, which consists of oxygen are hydroxyl radicals
-
-
-
- Superoxide anion radical
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Hypochlorite
- Nitric oxide radical
- Peroxyntrite radical
-
-
Types of Free Radicals
Read more : Which Of The Following Is A Drawback Of Hearing Aids
Most organic radicals are quite unstable and very reactive. There are two kinds of radicals, neutral radicals and charged radicals as shown below.
Moreover, there are two types of radicals: the sigma radicals and the pi radicals. An unpaired electron in the sigma-radical is in the sigma orbital and an unpaired electron in the pi radical is in the pi orbital respectively. Therefore, the radicals above are pi radicals, t-Butyl radical is also pi radical since this radical is stabilized by the hyperconjugation. However, the phenyl radical and the vinyl radical are typical sigma radicals.
Normally, pi radicals are stabilized by the hyperconjugation effect or the resonance effect. However, sigma radicals are very reactive because there is no such stabilizing effect.
Uses of Free Radicals
-
-
-
- These highly reactive structures are present in the membranes of cells of damaging biologically relevant molecules such as the DNA, lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates etc.
- The free radicals attack important macromolecules which leads to cell damage and homeostatic disruption such as proteins, nucleic acids etc.
- Generally alkyl halides or aryl halides are used as radical precursors for R or Ar however halogenation of sugars and nucleosides which have many OH groups and other delicate functional groups is rather difficult.
- Barton Mccombie reaction is very useful for the radical reactions in sugars nucleosides and peptides.
- Other thiocarbonyl derivatives formed from alcohols with phenoxythiocarbonyl chloride, diimidazole etc can also be used instead of methyl xanthate.
-
-
Sources of Free Radicals
Free radicals are generated internally through the following sources.
-
-
-
- Mitochondria
- Inflammation
- Exercise
- Phagocytosis
- Peroxisomes
-
-
Free radicals are found externally in the following sources.
-
-
-
- Environmental pollution
- Cigarette smoke
- Radiation
- Drugs and pesticides
- Ozone layer
-
-
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH