Core Concepts
This tutorial is about the ether functional group. It will cover the structure of the ether group and the reactions that they participate in.
Topics Covered in Other Articles
- Functional Groups
- Ester Functional Group
- Amino Functional Group
What is the Ether Functional Group?
The ether group consists of an oxygen atom with an R group single-bonded to each side. These R groups can be the same, however, they are not always.
You are viewing: Which Of The Following Compounds Contains An Ether Functional Group
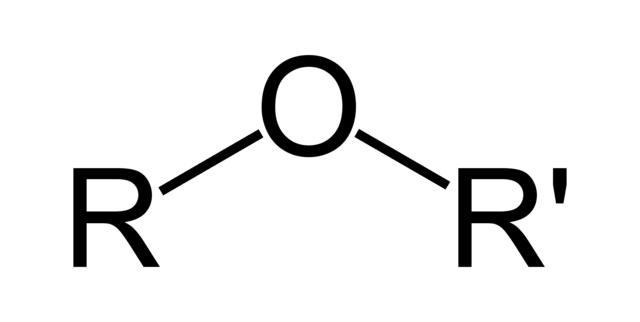
In an ether, the Oxygen must be bonded to carbon on both sides. If one of the R groups is a Hydrogen atom, then the compound is an alcohol.
Quick Facts on the Ether Group
- Structure: An Oxygen single bonded to two alkyl groups.
- Formula: R-O-R’
- Atomic Weight: ≥46.07 g/mol
- pH: Generally basic. Ethers can act as Lewis Bases because of the lone pairs on Oxygen
- pKa: When protonated, ethers have a pKa of about -3
- Diethyl ether is a common solvent
Naming Conventions
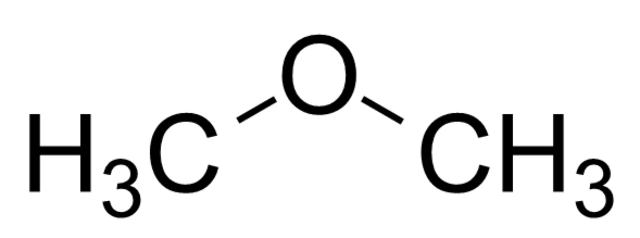
Naming ethers is fairly simple. The two R groups are named alphabetically, and the suffix “-ether” follows. If both R groups are the same, the prefix “di-” goes before the name of the R group. Below are some examples of ethers with their names.
Ether Group Reactions
Ethers participate in numerous reactions, more often as solvents than reactants. Ethers tend not to be reactive due to the difficulty of breaking the C-O single bonds. The most famous reaction involving ethers is the Williamson Ether Synthesis, in which an alkoxide reacts with an alkyl halide to form an ether.
Read more : Which Is More Reversible Vasectomy Vs Tubes Tied
Aside from their synthesis, ethers only react under specific circumstances. For example, epoxides are a type of ether in which the oxygen and the carbon atoms directly attached to it form a three-membered ring. Because the bond angles are small, the ring is strained and can be broken in either acidic or basic conditions.
Williamson Ether Synthesis
When a primary or secondary alkyl halide reacts with an alkoxide, the product of the reaction is an ether. One side of the ether is an alkyl chain from the alkyl halide, and the other side is an alkyl chain that came from the alkoxide. An alkoxide is any RO- group.
The alkyl halide must be primary or secondary because the synthesis proceeds as an SN2 reaction. For the nucleophilic alkoxide to perform the back-side attack on the alkyl halide, there must be enough space. This means that tertiary alkyl halides cannot undergo Williamson Ether syntheses.
Epoxide Formation and Opening
Epoxides are a type of ether. They are heterocyclic compounds that contain an oxygen and two carbon atoms. One way to form Epoxides is with the addition of a base and heat to a halohydrin. A halohydrin is a compound containing both an OH group and a halide.
Epoxides also form when an alkene reacts with meta-chloroperbenzoic acid, or m-CPBA.
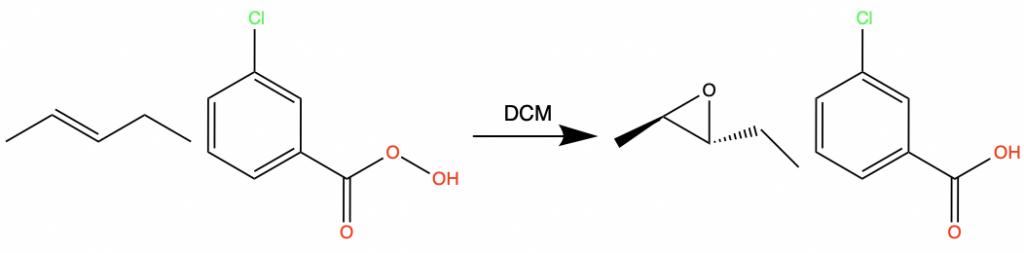
Epoxide rings can open under both acidic and basic conditions. In acidic conditions, the nucleophile attacks the ring on the more substituted side. The stereochemistry reverses at the electrophilic carbon.
Read more : Which Complex Number’s Graph Is Shown
In basic conditions, the nucleophile attacks the ring on the less substituted side.
Ethers as Solvents
Ethers serve as solvents in a variety of organic reactions. They are moderately polar and aprotic. This means that ethers can only accept hydrogen bonds.
Diethyl Ether
One of the most well-known examples of this functional group is diethyl ether. Diethyl ether is a useful solvent for a variety of reactions. Historically, it was used as an anesthetic. However, because of its flammability, alternatives to diethyl ether are more common. In modern industry, the cyclic ether tetrahydrofuran is more common than diethyl ether due to the latter’s flammability.
Diethyl ether is highly volatile. Even though it has a boiling point of 34.6°C, diethyl ether will evaporate rapidly when left in an open container.
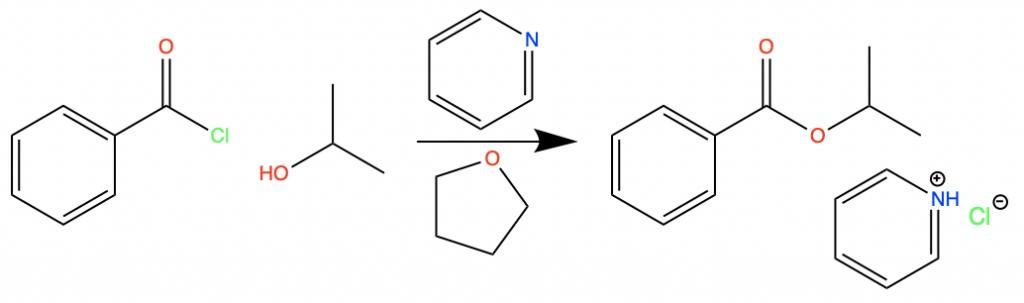
Ethereal solvents are often involved in the esterification of acid chlorides. This type of reaction is the replacement of a Chlorine atom next to a carbonyl group with an alkoxy group. An alkoxy group is any RO group where the oxygen connects the R group to the rest of the compound.
Practice Questions
- Draw the Structures of the following four ethers:
- diisopropyl ether
- cyclobutylmethyl ether
- Diphenyl ether
- Dicyclopentyl ether
Predict the product of the following reaction:

Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH
