Platonic solids, also known as regular solids or regular polyhedra, are solids with equivalent faces composed of congruent convex regular polygons. Platonic solids were studied by the ancient greek who also call these solids cosmic solids and are of 5 types. It is believed that the five platonic solids that exist in nature represent the five elements i.e. earth, air, fire, water, and the universe. Let us learn more about the platonic solids in geometry, the properties, the different types and solve a few examples.
1. Definition of Platonic Solids 2. Properties of Platonic Solids 3. Types of Platonic Solids 4. Proof of Existence of 5 Platonic Solids 5. FAQs on Platonic Solids
You are viewing: Which Of The Following Platonic Solids Is Also A Cube
A platonic solid is a 3D shape where each face is the same as a regular polygon and has the same number of faces meeting at each vertex. A regular, convex polyhedron with identical faces made up of congruent convex regular polygons is called a platonic solid. There are 5 different kinds of solids that are named by the number of faces that each solid has. These 5 solids are considered to be associated with the five elements of nature i.e. Earth, air, fire, water, and the universe. Plato, who was studying the platonic solids closely, associated each shape with nature. The 5 times of platonic solids are:
- Tetrahedron
- Cube
- Octahedron
- Dodecahedron
- Icosahedron
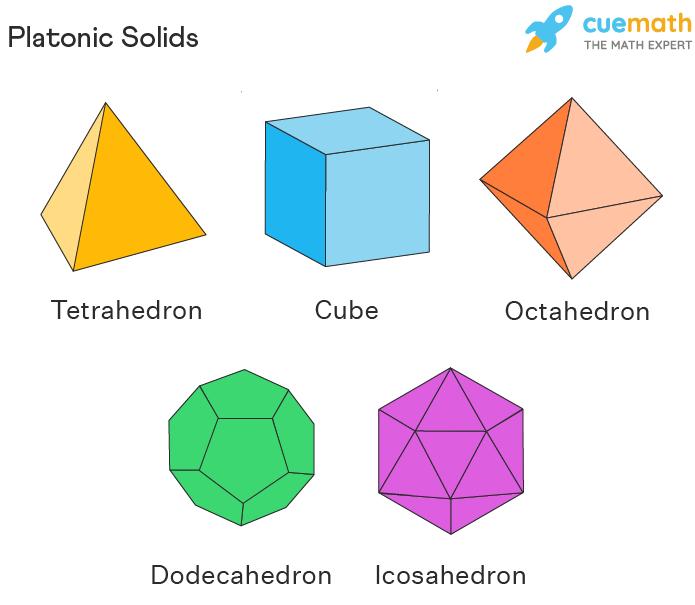
Plato associated the tetrahedron with fire, the cube with earth, the icosahedron with water, the octahedron with air, and the dodecahedron with the universe.
Platonic solids have their own unique properties that distinguish them from the rest. They are mentioned below:
- All the faces are regular and congruent.
- Platonic shapes are convex polyhedrons.
- Faces of platonic solid do not intersect except at their edges.
- The same number of faces meet at each vertex.
- Platonic solids have polygonal faces that are similar in form, height, angles, and edges.
- Platonic solids are three-dimensional, convex, and regular solids shapes.
There are 5 types of platonic solids with unique properties and different shapes. Let us learn more about the 5 types:
Tetrahedron
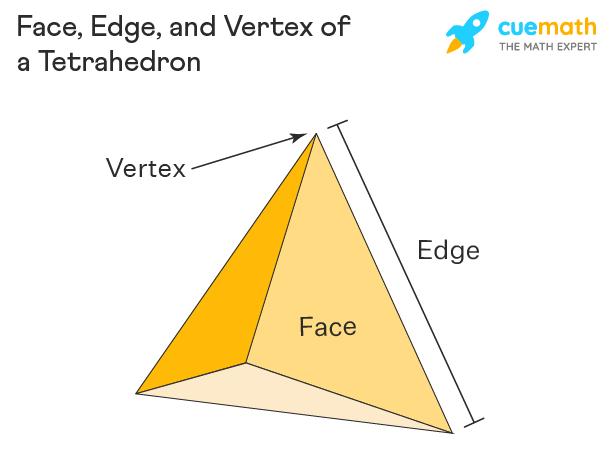
A tetrahedron is known as a triangular pyramid in geometry. The tetrahedron consists of 4 triangular faces, 6 straight edges, and 4 vertex corners. It is a platonic solid which has a three-dimensional shape with all faces as triangles. The properties of a tetrahedron are:
- A tetrahedron has 4 faces, 6 edges, and 4 vertices (corners).
- All four vertices are equidistant from each other.
- It has 6 planes of symmetry.
- Unlike other platonic solids, a tetrahedron has no parallel faces.
- A regular tetrahedron has equilateral triangles for all its faces.
Cube
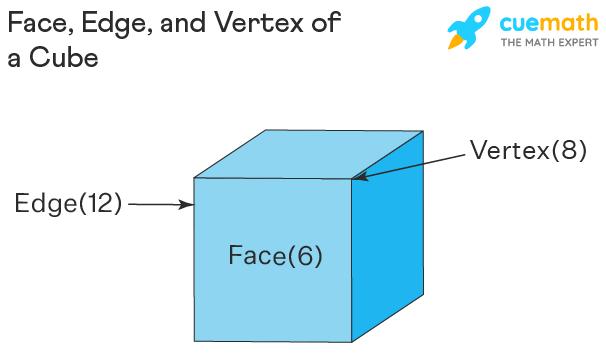
A cube is a 3D solid object with 6 square faces and all the sides of a cube are of the same length. The cube is also known as a regular hexahedron that is a box-shaped solid with 6 identical square faces. The properties of a cube are:
- A cube consists of 12 edges, 6 faces, and 8 vertices.
- The faces of a cube are square-shaped which means the length, breadth, and height are the same.
- The angles between any two faces or surfaces are 90°.
- The opposite faces and edges are parallel to each other.
- Each of the faces meets the other four faces.
- Each of the vertices meets the three faces and three edges.
Octahedron
Read more : Which Is Worse Frozen Shoulder Or Rotator Cuff Tear
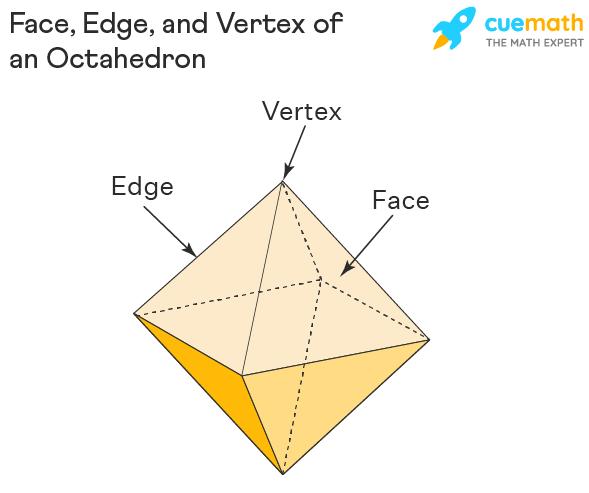
An octahedron is a polyhedron with 8 faces, 12 edges, and 6 vertices and at each vertex 4 edges meet. The faces of an octahedron are shaped like an equilateral triangle. The properties of an octahedron are:
- An octahedron has 6 vertices and at each vertex 4 edges meet.
- An octahedron has 8 faces shaped like an equilateral triangle, in the case of a regular octahedron.
- An octahedron has 12 edges.
Dodecahedron
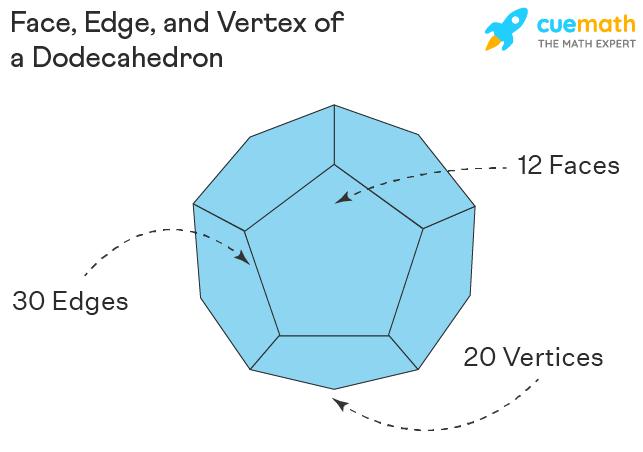
A dodecahedron is a platonic solid that consists of 12 sides and 12 pentagonal faces. The properties of a dodecahedron are:
- A dodecahedron has 12 pentagonal sides, 30 edges, and 20 vertices and at each vertex 3 edges meet.
- The platonic solid has 160 diagonals.
- Dodecahedron shapes can be seen in many real-life situations like the Roman dodecahedron, dodecahedron dice, etc.
Icosahedron
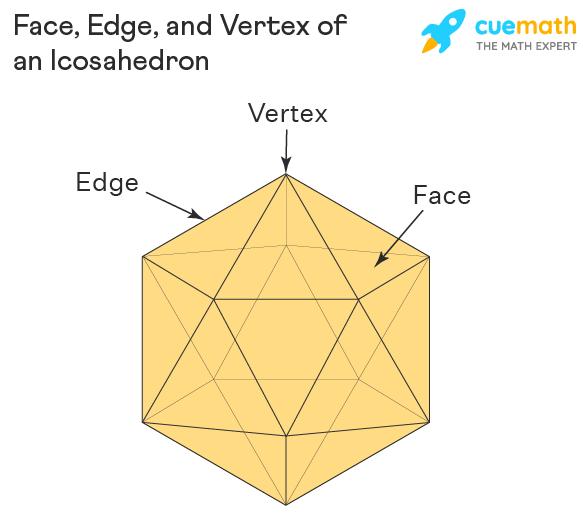
An icosahedron is a platonic solid with 20 faces, The icosahedron’s definition is derived from the ancient Greek words Icos (eíkosi) meaning ‘twenty’ and hedra (hédra) meaning ‘seat’. The properties of an icosahedron are:
- Icosahedron has 20 faces, 30 edges, and 12 vertices.
- The shape consists of equilateral triangle faces.
- It has the greatest volume for its surface area of any platonic solid.
- It has the greatest number of faces of any platonic solid.
Platonic solids are considered to be only 5 solid shapes. Here are the reasons why there are only 5 shapes and not more:
- For each of the 5 shapes, at each vertex at least 3 faces meet.
- The internal angles that meet at a vertex are less than 360°.
- All 5 shapes flatten at 360°.
Platonic Solid Meet at Vertex Angles at Vertex (less than 360°) Tetrahedron 3 regular triangles meet
Internal angles = 60°
60 × 3 = 180°
Cube 3 squares meet
Internal angles = 90°
Read more : Which Reports Require The Activation Of Advertising Features
90 × 3 = 270°
Octahedron 4 regular triangles meet
Internal angles = 60°
60 × 4 = 240°
Dodecahedron 3 pentagons meet
Internal angles = 108°
108 × 3 = 324°
Icosahedron 5 regular triangles meet
Internal angles = 60°
60 × 5 = 300°
Euler’s Formula for Proof of Existence
According to Euler’s formula, for any convex polyhedron, the Number of Faces plus the Number of Vertices (corner points) minus the Number of Edges always equals 2. Which is written as F + V – E = 2. Let us take apply this in one of the platonic solids – Icosahedron. Icosahedron has 20 faces, 30 edges, and 12 vertices, hence F + V – E = 20 + 12 – 30 = 2.
Related Topics
Here are a few topics related to the platonic solids, do take a look.
- Pentagon
- Geometry
- 2D shapes
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH