The addition property of equality states that when the same quantity is added to both sides of an equation, the equation does not change. If a number x is added to both sides of an equation A = B, then the equation still holds true. It can be expressed mathematically as, A + x = B + x. Let us learn more about the addition property of equality in this article along with its formula. We shall also discuss the addition property of equality for fractions.
1. What is Addition Property of Equality? 2. Addition Property of Equality Formula 3. Addition Property of Equality with Fractions 4. FAQs on Addition Property of Equality
You are viewing: Which Property Of Equality Was Used To Solve This Equation
The addition property of equality is defined as “When the same amount is added to both sides of an equation, the equation still holds true”. It is a very important and one of the common properties of equality in mathematics. The other properties are the subtraction property, multiplication property, and division property of equality.
The addition property of equality is used while solving equations. For example, to solve x – 3 = 5, we have to add 3 to both sides so that only the variable (x) will be left on the left side. This implies, x – 3 + 3 = 5 + 3, which can be simplified as x = 8. Let us learn the addition property of equality formula in the next section.
The formula for the addition property of equality is given below:
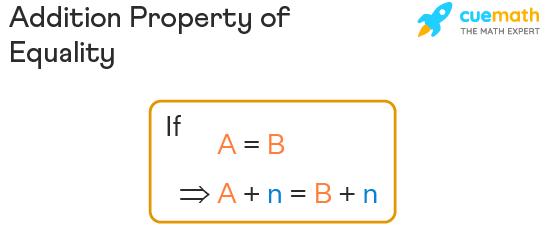
If the given equation is A = B, and the same quantity n is added to both sides of this equation, we get A + n = B + n, which is true and satisfies the equation. We can use this property of equality in arithmetic equations as well as in algebraic equations. In the case of an arithmetic equation, for example, 2 + 3 = 5, if we add a number to both sides, say 7, the equation will still be true. Let’s verify it.
Read more : Which Real Estate Agency To Join In Singapore
2 + 3 + 7 = 5 + 7
L.H.S = 2 + 3 + 7 = 12
R.H.S = 5 + 7 = 12
Therefore, L.H.S = R.H.S.
Let us take one more example of an algebraic equation, x – 4 = 12. It can be solved using the addition property of equality, as shown below.
x – 4 = 12
By adding 4 to both sides of the equation, we get, x – 4 + 4 = 12 + 4.
Read more : Which Of The Following Characters Precedes Excel Functions
⇒ x = 16
Therefore, the value of x is 16. It is the application of the addition property of equality in math.
The addition property of equality works with fractions as well. The same integer or fraction can be added to an equation containing fractions. For example, if 2x/3 + 5/6 = y + 5/6, this implies that 2x/3 = y. The general form of addition property of equality with fractions is written below:
A/B + x/y = C/D + x/y
Here, A/B = C/D is the given equation and x/y is the fraction added to both sides without changing the equality.
Important Notes on Addition Property of Equality
- The addition property of equality states that when the same number is added on both sides of an equation, the equality still holds.
- The formula for the addition property of equality is given by, A = B ⇒ A + n = B + n.
- The property holds for numbers with fractions.
► Related Articles
- Associative Property of Addition
- Transitive Property
- Solving Linear Equations
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHICH
