A triangle in which one of the interior angles is 90° is called a right triangle. The longest side of the right triangle, which is also the side opposite the right angle, is the hypotenuse and the two arms of the right angle are the height and the base. Here’s what a right triangle looks like:
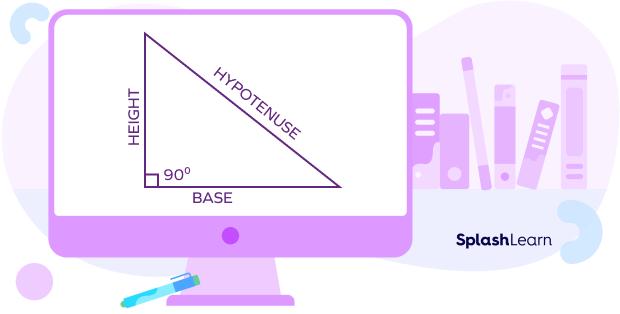
The total space or territory covered by a right-angled triangle is known as the area of a right triangle. It’s calculated in square units. The units m2, cm2, in2, yd2, and others commonly represent the area.
You are viewing: Which Triangle Must Be A Right Triangle And Why
Features of a Right Triangle
- The right angle is always the largest angle in a right triangle.
- The hypotenuse, the side opposite the right angle, is the longest side.
- There can’t be any obtuse angles in a right triangle.
Types of Right Triangles
Broadly, right triangles can be categorized as:
1. Isosceles right triangle: In this triangle, one interior angle measures 90°, and the other two angles measure 45° each. It is also known as a 45-90-45 triangle.
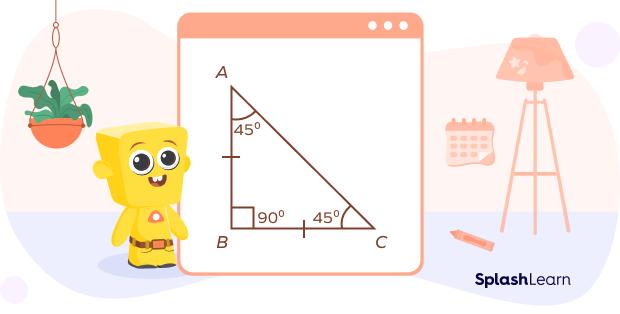
This is an isosceles right triangle, with the sides AB and AC equal and ∠B measuring 90°. Here, ∠A and ∠C measure 45° each because the property states that angles opposite to equal sides are also equal.
2. Scalene right triangle: This triangle is the one in which one interior angle measures 90°, while the other two have different measures. For example:
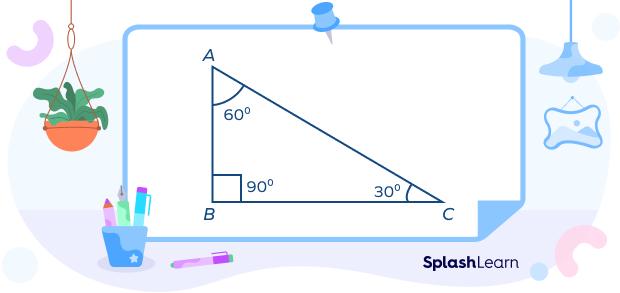
In the scalene right triangle ABC, ∠A measures 30°, ∠B measures 90°, and ∠C measures 60°. In this triangle, all the three sides will be of different lengths, and the three angles will be of different measures.
The Formula for a Right-Angled Triangle
Pythagoras theorem
- Pythagoras discovered that the hypotenuse square equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides in a right-angled triangle.
The perimeter of a right triangle
The perimeter of a right-angled triangle is defined as the total length of the boundary. The formula for perimeter is:
P (perimeter) = a + b + c (sum of the sides of a triangle)
Area of a right-angled triangle
The area of a right-angled triangle is defined as the space occupied by the triangle. The formula for the area is:
Area = $frac{1}{2}times basetimes height$
Solved Examples
- The largest side of a triangle is 10 cm. If the height of the triangle is 8 cm, determine the area using the Pythagorean theorem.
Solution:
The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right triangle.
Here, hypotenuse (H) = 10 cm, height (h) = 8 cm and the base (b) is unknown.
According to the Pythagoras theorem,
Read more : Why It Does Matter
H2 = b2 + h2
102 = b2 + 82
100 = b2 + 64
b2 = 36 cm2
b = $sqrt{36}$ = 6 cm
Area = $frac{1}{2}times basetimes height$
= $frac{1}{2}times 6times 8 = 24$
Therefore, the area of the triangle = 24 square cm.
- The sides of the triangle are in the ratio 3:4:5. The perimeter is 840 m. Find its area.
Solution:
Let the sides of the triangle be 3x, 4x, and 5x respectively.
We know that the perimeter = 840 m.
3x + 4x + 5x = 840
12x = 840
x = $frac{840}{12}$ = 70
So, the sides of the triangle are:
Read more : Why Did Humpty Dumpty Have A Great Fall
3x = 3(70) = 210 m
4x = 4(70) = 280 m
5x = 5(70) = 350 m
Since 350 m is the longest side of the triangle, it is the hypotenuse.
So, 210 m and 280 m are the base and the height of the triangle interchangeably.
Using the formula for the area of the right triangle, we get
Area = $frac{1}{2}times basetimes height = frac{1}{2}times 210times 280 = 29,400$
Therefore, the area of the given triangle = 29,400 m2
- What is the measure of the hypotenuse in a right triangle that has a height equal to 7 cm and the base equal to 5 cm?
Solution:
Perpendicular height (h) = 7 cm, Base (b) = 5 cm and Hypotenuse (H) = ?
By Pythagoras Theorem,
H2 = b2 + p2
H2 = 52 + 72
H2 = 25 + 49
H2 = 74H = $sqrt{74}$ cm
Practice Problems
Frequently Asked Questions
Source: https://t-tees.com
Category: WHY
